In hierarchical model, data is organized into a tree like structure with each record is having one parent record and many children. The main drawback of this model is that, it can have only one to many relationships between nodes.
Note: Hierarchical models are rarely used now.
Sample Hierarchical Model Diagram:
Lets say we have few students and few courses and a course can be assigned to a single student only, however a student take any number of courses so this relationship becomes one to many.
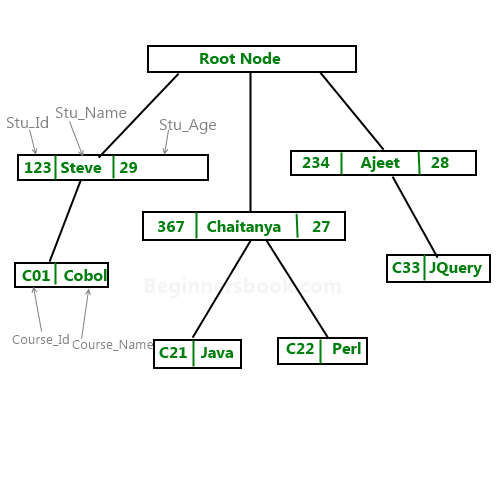
Example of hierarchical data represented as relational tables: The above hierarchical model can be represented as relational tables like this:
| Stu_Id | Stu_Name | Stu_Age |
| 123 | Steve | 29 |
| 367 | Chaitanya | 27 |
| 234 | Ajeet | 28 |
Course Table:
| Course_Id | Course_Name | Stu_Id |
| C01 | Cobol | 123 |
| C21 | Java | 367 |
| C22 | Perl | 367 |
| C33 | JQuery | 234 |
Leave a Reply