DBMS is a software that manages the data for efficient storage and fast retrievals of data from database. MySQL, IBM Db2, Oracle, PostgreSQL etc. are all DBMS softwares that manages the data. In this guide, you will learn various types of DBMS (Database Management System).
Types of DBMS
There are 4 types of DBMS:
1. Relational Database Management System (RDBMS)
2. Object Oriented Database Management System.
3. Hierarchical Database management system.
4. Network Database management system.
1. Relational Database Management System
In RDBMS, data is stored in tables, in form of rows and columns, where a row represent the record of the data and column represents the attributes of the record.
For example, a student table stores the records of various students, a row of this table represents the record of a single student and the column represents the attributes of the record such as student id, name, age, address etc.
Student table
ID Name Age Address --- --------- ---- -------- 101 Ajeet 28 Delhi 102 Chaitanya 32 Noida 103 Hari 31 Pune 104 Rahul 30 Agra 105 Steve 35 Noida
We use SQL to manage, organize and perform various operations on RDBMS.
Examples of RDBMS: MySQL, Oracle, DB2 etc.
2. Object Oriented Database Management System
Data is stored as objects, attributes and methods. It typically stores and manages objects directly on the database server’s disk. There are no tables, no rows, no columns, no foreign keys. There are only objects.
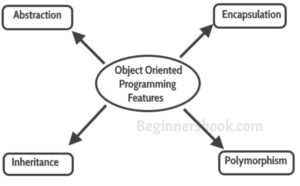
Elements of Object Oriented Database:
Object: It is a combination of data and its behaviour(commonly referred as methods).
For example: A house is an object. An object has two characteristics: states and behaviour.
In this example of “House” being an object. The state of “House” is its address, color, area etc. and behaviour is Open main door, close main door etc.
An object oriented database can be represented by the following diagram. To read more about object oriented programming, refer this guide.
3. Hierarchical Database Management System
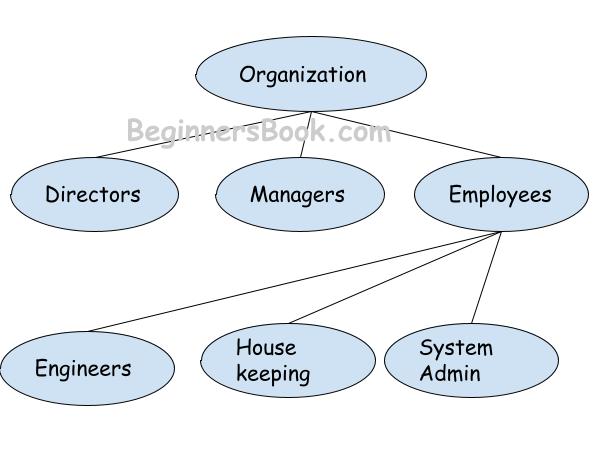
In hierarchical database management system, data is stored in form of one to many relationships. You can visualize it like a tree where a root node is attached to several descendants nodes called leaves.
Example of Hierarchical database systems are: IMS by IDM, Windows registry by Microsoft.
For example: To store the data of an organization, the root node is organization itself. The immediate child nodes are: Employees, Managers, Directors. These child nodes can have further child nodes such as Employees can have child nodes such as: Engineers, Housekeeping staff, system admin etc.
It can be represented by the following diagram:
4. Network Database Management System
A network database management system (network DBMS) is based on a network data model, which allows each record to be related to multiple primary records and multiple secondary records.
A network database is based on a traditional hierarchical database, except it allows each object to have multiple parents instead of a single parent. This means data in network database can have one to one or one to many relationships.