Constructor is a block of code that initializes the newly created object. A constructor resembles an instance method in java but it’s not a method as it doesn’t have a return type. In short constructor and method are different(More on this at the end of this guide). People often refer constructor as special type of method in Java.
Constructor has same name as the class and looks like this in a java code.
public class MyClass{
//This is the constructor
MyClass(){
}
..
}
Note that the constructor name is same as class name and it doesn’t have a return type.
Table of Contents
- How does constructor work?
- A simple constructor program in java
- Types of Constructors
- What if there is only parameterized constructor in the class
- Constructor chaining
- super()
- Constructor Overloading
- Java copy constructor
- Difference between constructor and method
- Summary
1. How does a constructor work?
To understand the working of constructor, lets take an example. lets say we have a class MyClass.
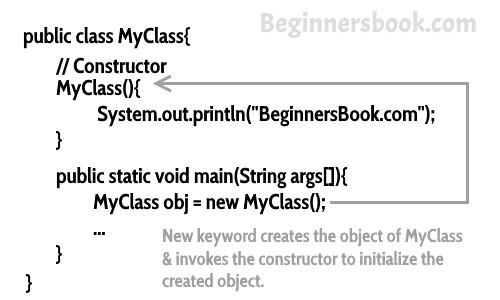
When we create the object of MyClass like this:
MyClass obj = new MyClass()
The new keyword here creates the object of class MyClass and invokes the constructor to initialize this newly created object.
You may get a little lost here as I have not shown you any initialization example, lets have a look at the code below:
2. A simple constructor program in java
Here we have created an object obj of class Hello and then we displayed the instance variable name of the object.
As you can see that the output is BeginnersBook.com which is what we have passed to the name during initialization in constructor. This shows that when we created the object obj the constructor got invoked.
In this example we have used this keyword, which refers to the current object, object obj in this example. We will cover this keyword in detail in the next tutorial.
public class Hello {
String name;
//Constructor
Hello(){
this.name = "BeginnersBook.com";
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Hello obj = new Hello();
System.out.println(obj.name);
}
}
Output:
BeginnersBook.com
3. Types of Constructors
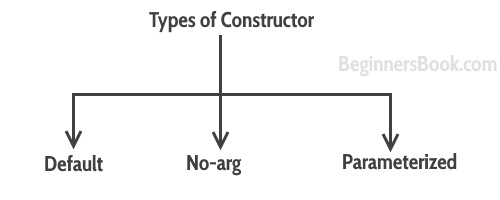
There are three types of constructors: Default, No-arg constructor and Parameterized.
3.1 Default constructor
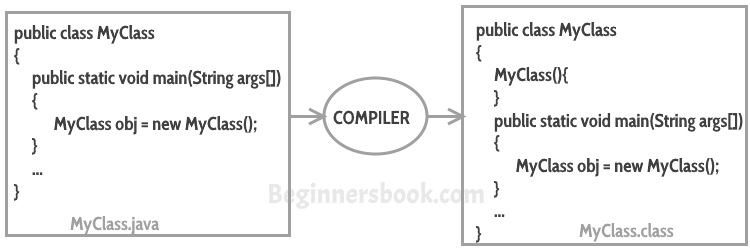
If you do not implement any constructor in your class, Java compiler inserts a default constructor into your code on your behalf. This constructor is known as default constructor. You would not find it in your source code(the java file) as it would be inserted into the code during compilation and exists in .class file. This process is shown in the diagram below:
If you implement any constructor then you no longer receive a default constructor from Java compiler.
3.2 no-arg constructor:
Constructor with no arguments is known as no-arg constructor. The signature is same as default constructor, however body can have any code unlike default constructor where the body of the constructor is empty.
Although you may see some people claim that that default and no-arg constructor is same but in fact they are not, even if you write public Demo() { } in your class
Demoit cannot be called default constructor since you have written the code of it.
Example: no-arg constructor
class Demo
{
public Demo()
{
System.out.println("This is a no argument constructor");
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
new Demo();
}
}
Output:
This is a no argument constructor
3.3 Parameterized constructor
Constructor with arguments(or you can say parameters) is known as Parameterized constructor.
Example: parameterized constructor
In this example we have a parameterized constructor with two parameters id and name. While creating the objects obj1 and obj2 I have passed two arguments so that this constructor gets invoked after creation of obj1 and obj2.
public class Employee {
int empId;
String empName;
//parameterized constructor with two parameters
Employee(int id, String name){
this.empId = id;
this.empName = name;
}
void info(){
System.out.println("Id: "+empId+" Name: "+empName);
}
public static void main(String args[]){
Employee obj1 = new Employee(10245,"Chaitanya");
Employee obj2 = new Employee(92232,"Negan");
obj1.info();
obj2.info();
}
}
Output:
Id: 10245 Name: Chaitanya Id: 92232 Name: Negan
Example2: parameterized constructor
In this example, we have two constructors, a default constructor and a parameterized constructor. When we do not pass any parameter while creating the object using new keyword then default constructor is invoked, however when you pass a parameter then parameterized constructor that matches with the passed parameters list gets invoked.
class Example2
{
private int var;
//default constructor
public Example2()
{
this.var = 10;
}
//parameterized constructor
public Example2(int num)
{
this.var = num;
}
public int getValue()
{
return var;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Example2 obj = new Example2();
Example2 obj2 = new Example2(100);
System.out.println("var is: "+obj.getValue());
System.out.println("var is: "+obj2.getValue());
}
}
Output:
var is: 10 var is: 100
What if you implement only parameterized constructor in class
class Example3
{
private int var;
public Example3(int num)
{
var=num;
}
public int getValue()
{
return var;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Example3 myobj = new Example3();
System.out.println("value of var is: "+myobj.getValue());
}
}
Output: It will throw a compilation error. The reason is, the statement Example3 myobj = new Example3() is invoking a default constructor which we don’t have in our program.
When you don’t implement any constructor in your class, a default constructor is added to the class during compilation, however when you implement any constructor (in above example I have implemented parameterized constructor with int parameter), then you don’t receive the default constructor by compiler into your code.
If we remove the parameterized constructor from the above code then the program would run fine, because then compiler would insert the default constructor into your code.
Constructor Chaining
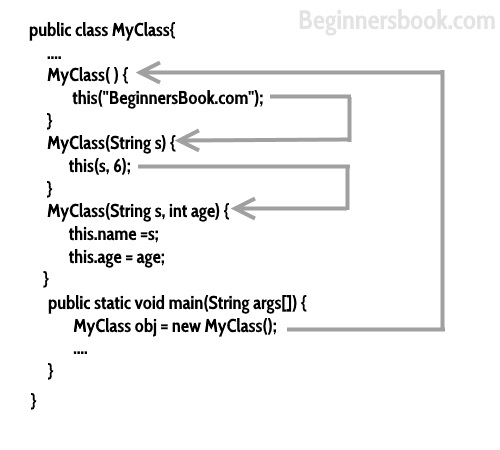
When A constructor calls another constructor of same class then this is called constructor chaining. In the above diagram, you can see that the default constructor is internally calling the constructor with string argument, this constructor is again calling a different constructor with two arguments. This is an example of constructor chaining. Read more about it at Constructor Chaining Explained with Example.
Super()
Whenever a child class constructor gets invoked it implicitly invokes the constructor of parent class. You can also say that the compiler inserts a super(); statement at the beginning of child class constructor.
class MyParentClass {
MyParentClass(){
System.out.println("MyParentClass Constructor");
}
}
class MyChildClass extends MyParentClass{
MyChildClass() {
System.out.println("MyChildClass Constructor");
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
new MyChildClass();
}
}
Output:
MyParentClass Constructor MyChildClass Constructor
Read more about super keyword here.
Constructor Overloading
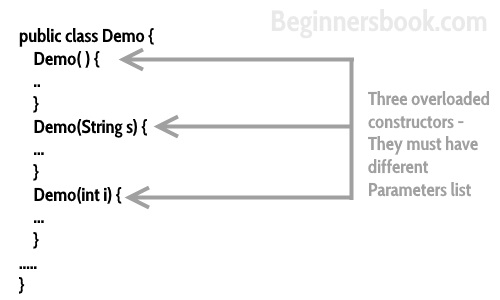
Constructor overloading is a concept of having more than one constructor with different parameters list, in such a way so that each constructor performs a different task.
Refer constructor overloading with example for more details with example.
Java Copy Constructor
A copy constructor is used for copying the values of one object to another object. Java doesn’t have a concept of copy constructor like C++, however there are certain ways by which you can copy the values of one object to another object:
- By creating a parameterized constructor with class reference as parameter.
- By using clone() method of the Object class.
- By assigning the values from one object to another object.
class JavaExample{
String web;
JavaExample(String w){
web = w;
}
/* This is the Copy Constructor, it
* copies the values of one object
* to the another object (the object
* that invokes this constructor)
*/
JavaExample(JavaExample je){
web = je.web;
}
void disp(){
System.out.println("Website: "+web);
}
public static void main(String args[]){
JavaExample obj1 = new JavaExample("BeginnersBook");
/* Passing the object as an argument to the constructor
* This will invoke the copy constructor
*/
JavaExample obj2 = new JavaExample(obj1);
obj1.disp();
obj2.disp();
}
}
Output:
Website: BeginnersBook Website: BeginnersBook
Difference between Constructor and Method
I know I should have mentioned it at the beginning of this guide but I wanted to cover everything in a flow. Hope you don’t mind :)
- The purpose of constructor is to initialize the object of a class while the purpose of a method is to perform a task by executing java code.
- Constructors cannot be abstract, final, static and synchronised while methods can be.
- Constructors do not have return types while methods do.
Quick Recap
- Every class has a constructor whether it’s a normal class or a abstract class.
- Constructors are not methods and they don’t have any return type.
- Constructor name should match with class name .
- Constructor can use any access specifier, they can be declared as private also. Private constructors are possible in java but there scope is within the class only.
- Like constructors method can also have name same as class name, but still they have return type, though which we can identify them that they are methods not constructors.
- If you don’t implement any constructor within the class, compiler will do it for.
- this() and super() should be the first statement in the constructor code. If you don’t mention them, compiler does it for you accordingly.
- Constructor overloading is possible but overriding is not possible. Which means we can have overloaded constructor in our class but we can’t override a constructor.
- Constructors can not be inherited.
- If Super class doesn’t have a no-arg(default) constructor then compiler would not insert a default constructor in child class as it does in normal scenario.
- Interfaces do not have constructors.
- Abstract class can have constructor and it gets invoked when a class, which implements interface, is instantiated. (i.e. object creation of concrete class).
- A constructor can also invoke another constructor of the same class – By using this(). If you want to invoke a parameterized constructor then do it like this: this(parameter list).
More on Constructor:
Roney Khan says
very very useful ….
mrs.rupali says
concepts explained in a simple and effective manner, its very nice as all small minute discussions are also provided and explained in a systematic way with examples ,this site really helps beginners to have good knowledge of java .
pallavi says
its very good for interview purpose , its awesome
jemima says
hi sir,
can u explain more clearly abt this() nd super() usage! plz!!
ankit dange says
My question is what is copy constructor in java programming and how to implement this basic concept.
Chetan says
Awesome tutorial you have explained all the concept with practically step by step:- keep it good work
VIGNESH ARUNACHALAM says
hi sir,it’s very useful.easy to learn.can you explain more clearly about method overriding in java with example and it’s usage! please!!
ram says
extraordinary site no need to go another institutes
Chenna says
Very helpful while preparing for a java interview
Gabriel D. says
Clear and aired written.
Thank you!
medha says
what will we get the output if we write super(“calling super one”)?
Surabhi says
What happens when super class only has parameterized constructors and child constructor does not evoke super(parameter) explicitly?
Solomon Nyatepe says
Great, pls I am a graphic designer and beginning to learn programming, can you pls help me understand the basics such as objects, methods
Tahseen Ali says
I t was worth a read! really learnt a lot … keep the good work up! :)
Santosh Reddy says
Hii,Chaitanya please provide next page option at the bottom.so that it will be easy for the readers.
Thank you
Chaitanya Singh says
I am working on it. I am updating the old guides and tutorials with the latest info and diagrams. Along with this I am adding next and prev links at the end of each guide. It will take some time. Thanks for sharing the concern. Happy Learning!