Continue statement is mostly used inside loops. Whenever it is encountered inside a loop, control directly jumps to the beginning of the loop for next iteration, skipping the execution of statements inside loop’s body for the current iteration. This is particularly useful when you want to continue the loop but do not want the rest of the statements(after continue statement) in loop body to execute for that particular iteration.
Syntax:
continue word followed by semi colon.
continue;
Example: continue statement inside for loop
public class ContinueExample {
public static void main(String args[]){
for (int j=0; j<=6; j++)
{
if (j==4)
{
continue;
}
System.out.print(j+" ");
}
}
}
Output:
0 1 2 3 5 6
As you may have noticed, the value 4 is missing in the output, why? because when the value of variable j is 4, the program encountered a continue statement, which makes it to jump at the beginning of for loop for next iteration, skipping the statements for current iteration (that’s the reason
printlndidn’t execute when the value of j was 4).
Flow Diagram of Continue Statement
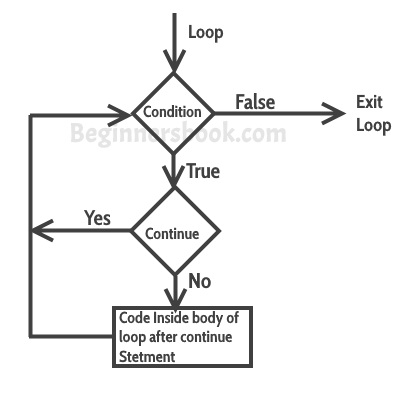
Example: Use of continue in While loop
Same thing you can see here. We are iterating this loop from 10 to 0 for counter value and when the counter value is 7 the loop skipped the print statement and started next iteration of the while loop.
public class ContinueExample2 {
public static void main(String args[]){
int counter=10;
while (counter >=0)
{
if (counter==7)
{
counter--;
continue;
}
System.out.print(counter+" ");
counter--;
}
}
}
Output:
10 9 8 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Example of continue in do-While loop
public class ContinueExample3 {
public static void main(String args[]){
int j=0;
do
{
if (j==7)
{
j++;
continue;
}
System.out.print(j+ " ");
j++;
}while(j<10);
}
}
Output:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 8 9
Leave a Reply