In this tutorial, you will learn the difference between JDK, JRE and JVM.
JDK (Java Development Kit)
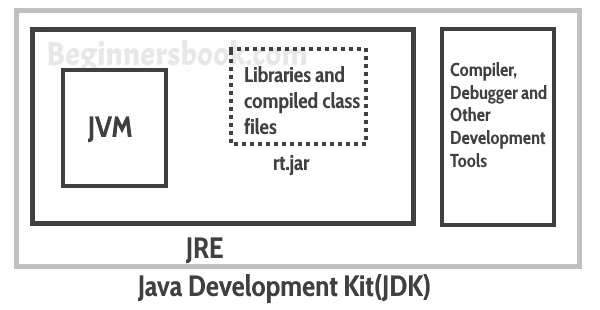
JDK is a superset of JRE, it contains everything that JRE has along with development tools such as compiler, debugger etc.
- JDK stands for Java Development Kit. To install Java on your system, you need to first install JDK on your system.
- JDK contains the tools that you need, in order to write and execute java programs.
- JDK consists of Private JRE, JVM, compiler, Java application launcher, Appletviewer, etc. It also provides the Standard Edition (SE) of java API.
Features of JDK
- The JDK comes with a complete Java Runtime Environment (JRE), that is different from the regular JRE thats the reason it is usually called a private runtime so we can say that it includes all the features that JRE has.
- It has all the java development tools such as compiler, JVM, JRE, debugger etc.
- You need jdk in order to write and run java program.
- JDK supports multiple platforms and can be installed on Windows, Mac and other operating systems.
JRE (Java Runtime Environment)
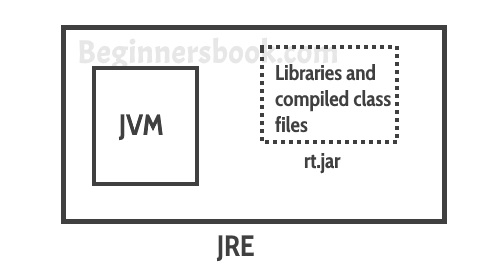
JRE is the environment within which the java virtual machine runs. JRE contains Java virtual Machine(JVM), class libraries, and other files excluding development tools such as compiler and debugger.
Which means you can run the code in JRE but you can’t develop and compile the code in JRE.
- JRE stands for Java Runtime Environment. It provides runtime environment for java applications.
- You need JRE in order to run java programs. If you are not a developer and not writing java programs, you do not need JDK but you still need JRE to run java programs.
- All the JDK already comes with JRE so you do not need to download and install it separately.
- JRE contains set of libraries and other files that JVM uses at runtime.
Features of JRE
- JRE contains set of libraries and other tools that JVM needs at runtime.
- You can easily run any java program on JRE but you need jdk to write and compile java programs.
- JRE contains libraries that are required for integrations such as Java Database Connectivity (JDBC), Java Naming and Directory Interface (JNDI), Remote Method Invocation (RMI) etc.
JVM (Java Virtual Machine)
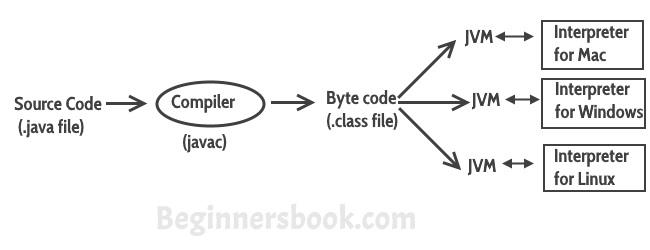
Java is a high level programming language. A program written in high level language cannot be run on any machine directly. First, it needs to be translated into that particular machine language. The javac compiler does this thing, it takes java program (.java file containing source code) and translates it into machine code (referred as byte code or .class file).
Java Virtual Machine (JVM) is a virtual machine that resides in the real machine (your computer) and the machine language for JVM is byte code. This makes it easier for compiler as it has to generate byte code for JVM rather than different machine code for each type of machine. JVM executes the byte code generated by compiler and produce output. JVM is the one that makes java platform independent.
Features of JVM
- JVM makes it possible to run java code on any machine, it is the JVM that makes java truly platform independent.
- It also allows to run java applications on cloud platforms.
- JDK and JRE both of these contain JVM.
- JVM is an interpreter as it executes the java code line by line.
- JVM converts the bytecode into machine code. JVM is platform independent as JVM doesn’t depend on the hardware and operating system of the machine.
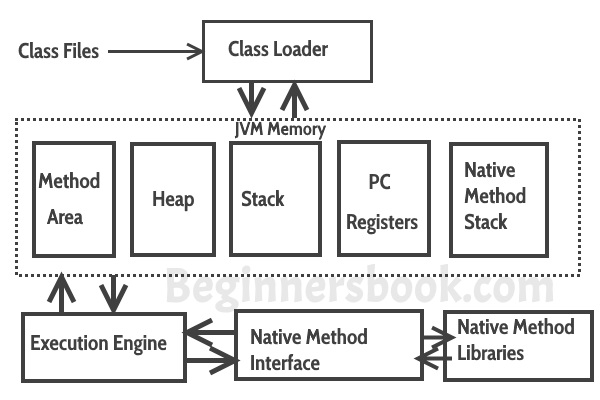
How JVM works?
JVM Architecture
Difference between JDK, JRE and JVM
| JDK | JRE | JVM |
|---|---|---|
| JDK stands for Java Development Kit | JRE stands for Java Runtime Environment | JVM stands for Java Virtual Machine. |
| It contains everything that JRE has along with development tools such as compiler, debugger etc. | JRE contains Java virtual Machine(JVM), class libraries, and other files excluding development tools such as compiler and debugger. | Java Virtual Machine (JVM) is a virtual machine that resides in the real machine (your computer) and the machine language for JVM is byte code |
| JDK is a superset of JRE | It is a subset of JDK. | JVM is a subset of JRE. |
| JDK is used to create and compile Java programs. | JRE is a part of JDK that contains JVM. | JVM is used to run the java code on any machine. |
Leave a Reply