Inheritance is one of the useful feature of OOPs. It allows a class to inherit the properties and methods of another class. A class inheriting properties and methods of another class can use those without declaring them.
The main purpose of inheritance in java is to provide the reusability of code so that a class has to write only the unique features and rest of the common properties and functionalities can be inherited from the another class.
Let’s understand this with a small example: In the following example, the Dog class extends (inherit) Animal class so that it can use the eat() method of Animal class. Similarly other classes like Cat, Horse etc. can extends this Animal class and use this method without rewriting this method.
// Parent class (Base class)
class Animal {
void eat() {
System.out.println("This animal eats food.");
}
}
// Child class (Derived class)
class Dog extends Animal {
void bark() {
System.out.println("The dog barks.");
}
}
// Main class to test inheritance
public class InheritanceExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog myDog = new Dog();
// Calling method from the parent class
myDog.eat();
// Calling method from the child class
myDog.bark();
}
}
Output:
This animal eats food.
The dog barks.
Now that we have seen a small example of inheritance, lets discuss this topic in detail with more such examples to understand this concept. Here we go..
Table of contents
The extends Keyword
A class can only inherit the fields (or properties) and methods of another class, if it extends the class. For example in the following snippet, class A extends class B. Now class A can access the fields and methods of class B.
class A extends B
{
}
Let’s learn the concept of parent and child class in Inheritance:
Child Class: The class that extends the features of another class is known as child class, sub class or derived class. In the above code, class A is the child class.
Parent Class: The class that shares the fields and methods with the child class is known as parent class, super class or Base class. In the above code, Class B is the parent class.
Advantages of Inheritance
- Inheritance removes redundancy from the code. A class can reuse the fields and methods of parent class. No need to rewrite the same redundant code again.
- Inheritance allows us to reuse of code, it improves reusability in your java application.
- Reduces code size: By removing redundant code, it reduces the number of lines of the code.
- Improves logical structure: Improves the logical structure of the code that allows programmer to visualize the relationship between different classes.
Also Read: OOPs Concepts
Syntax: Inheritance in Java
To inherit a class we use extends keyword. Here, class XYZ is a child class and class ABC is a parent class. The class XYZ is inheriting the properties and methods of ABC class.
class XYZ extends ABC
{
}
Terminologies used in Inheritance: To avoid confusion, let’s discuss the terminologies used in this guide.
- Super class and base class are synonyms of Parent class.
- Sub class and derived class are synonyms of Child class.
- Properties and fields are synonyms of Data members.
- Functionality is a synonym of method.
Inheritance Example in Java
In this example, we have a base class Teacher and a sub class PhysicsTeacher. Child class inherits the following fields and methods from parent class:
- Properties:
designationandcollegeNameproperties - Method:
does()
Child classes like MathTeacher, MusicTeacher and PhysicsTeacher do not need to write this code and can access these properties and method directly from base class. In this example, we are only reviewing PhysicsTeacher class.
Important: The main thing to note in this example is, that the child class PhysicsTeacher didn’t have to declare the does() method and didn’t have to declare the variables designation & collegeName.
class Teacher {
//fields of parent class
String designation = "Teacher";
String collegeName = "Beginnersbook";
//method of parent class
void does(){
System.out.println("Teaching");
}
}
public class PhysicsTeacher extends Teacher{
//field of child class
String mainSubject = "Physics";
public static void main(String args[]){
PhysicsTeacher obj = new PhysicsTeacher();
//accessing the fields of parent class
System.out.println(obj.collegeName);
System.out.println(obj.designation);
System.out.println(obj.mainSubject);
//accessing the method of parent class
obj.does();
}
}
Output:
Beginnersbook Teacher Physics Teaching
Based on the above example we can say that
PhysicsTeacherIS-ATeacher. This means that a child class has IS-A relationship with the parent class. This is why inheritance is known as IS-A relationship between child and parent class
Types of inheritance in Java
There are four types of inheritance in Java:
- Single
- Multilevel
- Hierarchical
- Hybrid
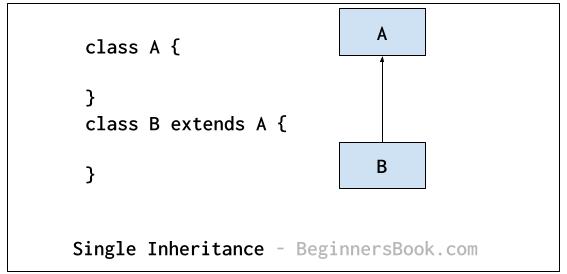
Single Inheritance
In Single inheritance, a single child class inherits the properties and methods of a single parent class. In the following diagram: class B is a child class and class A is a parent class.
Multilevel Inheritance
In multilevel inheritance, a parent class becomes the child class of another class. In the following diagram: class B is a parent class of C, however it is also a child class of A. In this type of inheritance, there is a concept of intermediate class, here class B is an intermediate class.

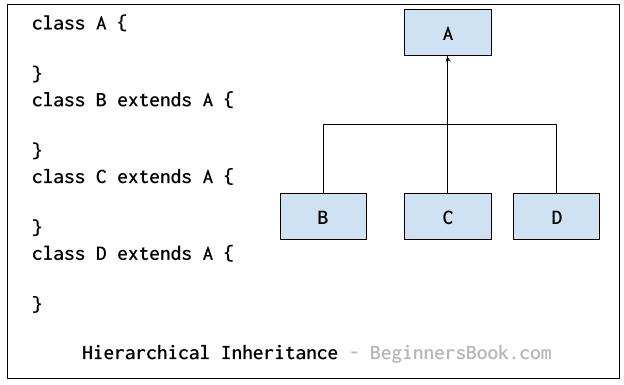
Hierarchical Inheritance
In hierarchical inheritance, more than one class extends the same class. As shown in the following diagram, classes B, C & D extends the same class A.
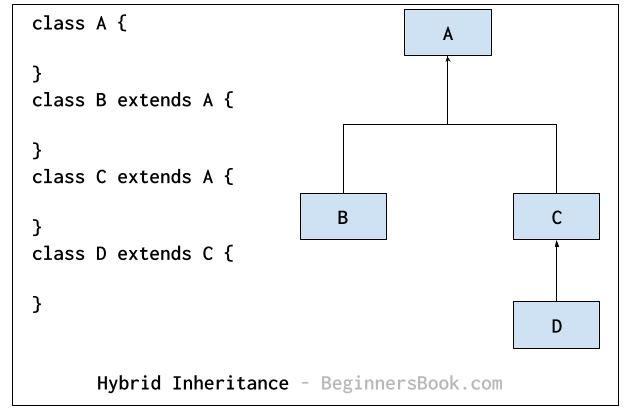
Hybrid Inheritance
Hybrid inheritance: Combination of more than one types of inheritance in a single program. For example class B & C extends A and another class D extends class C then this is a hybrid inheritance example because it is a combination of single and hierarchical inheritance.
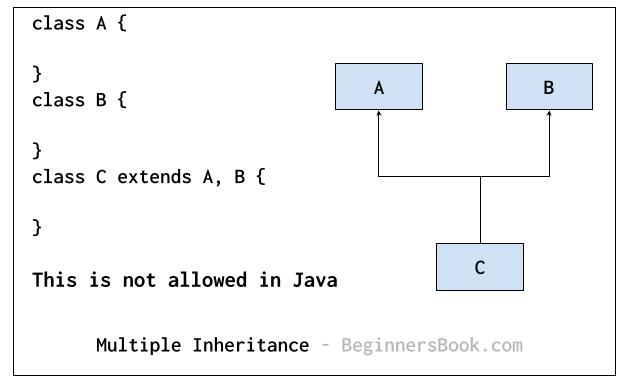
Multiple Inheritance
It refers to the concept of one class extending more than one classes, which means a child class has more than one parent classes. For example class C extends both classes A and B. Java doesn’t support multiple inheritance, read more about it here.
Java Inheritance instanceof keyword
The instanceof keyword returns true, if an object belongs to the class or its parent class.
class A{
}
class B extends A{
}
public class JavaExample extends B{
public static void main(String args[]) {
A obj1 = new A();
B obj2 = new B();
JavaExample obj3 = new JavaExample();
System.out.println(obj1 instanceof A);
System.out.println(obj2 instanceof A);
System.out.println(obj1 instanceof B);
System.out.println(obj3 instanceof B);
}
}
Output:
true true false true
Inheritance Access Specifier in Java
The derived class can inherit only those data members and methods of parent class, that are declared as public or protected.
If the members or methods of super class are declared as private then the derived class cannot access them. The private members can be accessed only in its own class. Such private members can only be accessed using public or protected getter and setter methods of super class as shown in the following example.
class Teacher {
private String designation = "Teacher";
private String collegeName = "Beginnersbook";
public String getDesignation() {
return designation;
}
protected void setDesignation(String designation) {
this.designation = designation;
}
protected String getCollegeName() {
return collegeName;
}
protected void setCollegeName(String collegeName) {
this.collegeName = collegeName;
}
void does(){
System.out.println("Teaching");
}
}
public class JavaExample extends Teacher{
String mainSubject = "Physics";
public static void main(String args[]){
JavaExample obj = new JavaExample();
/* Note: we are not accessing the data members
* directly we are using public getter method
* to access the private members of parent class
*/
System.out.println(obj.getCollegeName());
System.out.println(obj.getDesignation());
System.out.println(obj.mainSubject);
obj.does();
}
}
The output is:
Beginnersbook Teacher Physics Teaching
The important point to note in the above example is that the child class is able to access the private members of parent class through protected methods of parent class.
When we make a instance variable(data member) or method protected, this means that they are accessible only in the class itself and in child class. These public, protected, private etc. are all access specifiers and we have discussed them here: Access specifier in java.
How to use constructor in inheritance in java
constructor of sub class is invoked when we create the object of subclass, it by default invokes the default constructor of super class. Hence, in inheritance the objects are constructed top-down.
The superclass constructor can be called explicitly using the super keyword, but it should be first statement in a constructor. The super keyword refers to the superclass, immediately above of the calling class in the hierarchy. The use of multiple super keywords to access an ancestor class other than the direct parent is not permitted.
class ParentClass{
//Parent class constructor
ParentClass(){
System.out.println("Constructor of Parent");
}
}
class JavaExample extends ParentClass{
JavaExample(){
/* It by default invokes the constructor of parent class
* You can use super() to call the constructor of parent.
* It should be the first statement in the child class
* constructor, you can also call the parameterized constructor
* of parent class by using super like this: super(10), now
* this will invoke the parameterized constructor of int arg
*/
System.out.println("Constructor of Child");
}
public static void main(String args[]){
//Creating the object of child class
new JavaExample();
}
}
Output:
Constructor of Parent Constructor of Child
Inheritance and Method Overriding
When we declare the same method in child class, which is already present in the parent class then this is called method overriding. In such case, when we call the method from child class object, the child class version of the method is called. However we can call the parent class method using super keyword then it calls the parent class method as shown below:
class ParentClass{
//Parent class constructor
ParentClass(){
System.out.println("Constructor of Parent");
}
void disp(){
System.out.println("Parent Method");
}
}
class JavaExample extends ParentClass{
JavaExample(){
System.out.println("Constructor of Child");
}
void disp(){
System.out.println("Child Method");
//Calling the disp() method of parent class
super.disp();
}
public static void main(String args[]){
//Creating the object of child class
JavaExample obj = new JavaExample();
obj.disp();
}
}
The output is :
Constructor of Parent Constructor of Child Child Method Parent Method
Jerry says
this book has really been helpful to enhance my java knowledge. Its simple to understand and it gives good examples
sravanthi says
Its simple to understand and it provides good examples.