For loop is used to execute a set of statements repeatedly until a particular condition returns false. In Java we have three types of basic loops: for, while and do-while. In this tutorial you will learn about for loop in Java. You will also learn nested for loop, enhanced for loop and infinite for loop with examples.
Syntax of for loop:
for(initialization; condition ; increment/decrement)
{
statement(s);
}
Initialization: In the initialization part, variables like loop counter (you will generally see i and j in loops, these are the loop counters) are initialized. This is an optional part of the loop as the variables can be initialized before the loop. This executes only once when the loop starts.
Condition: This is one of the important part of the loop. This condition determines till when the loop should keep repeating. The loop keeps repeating until the condition becomes false.
Increment/Decrement: In this part of the loop declaration, you can specify the increment or decrement of loop counter. This is to modify the loop counter value so that at one point condition becomes false and the loop ends.
Statement: The statements inside the loop body keeps executing for each iteration of the loop until the loop stops.
Flow of Execution of the for Loop
As a program executes, the interpreter always keeps track of which statement is about to be executed. We call this the control flow, or the flow of execution of the program.
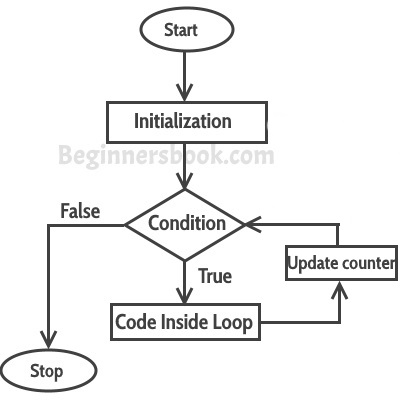
First step: In for loop, initialization happens first and only one time, which means that the initialization part of for loop only executes once.
Second step: Condition in for loop is evaluated on each iteration, if the condition is true then the statements inside for loop body gets executed. Once the condition returns false, the statements in for loop does not execute and the control gets transferred to the next statement in the program after for loop.
Third step: After every execution of for loop’s body, the increment/decrement part of for loop executes that updates the loop counter.
Fourth step: After third step, the control jumps to second step and condition is re-evaluated.
Example: Simple for loop
This is a simple example of for loop. Here we are displaying the value of variable i inside the loop body. We are using decrement operator in the loop so the value of i decreases by one after each iteration of the loop and at some point the condition i>1 returns false, this is when the loop stops.
class ForLoopExample {
public static void main(String args[]){
for(int i=10; i>1; i--){
System.out.println("The value of i is: "+i);
}
}
}
The output of this program is:
The value of i is: 10 The value of i is: 9 The value of i is: 8 The value of i is: 7 The value of i is: 6 The value of i is: 5 The value of i is: 4 The value of i is: 3 The value of i is: 2
In the above program:
int i=1 is initialization expression
i>1 is condition(Boolean expression)
i– Decrement operation
Java Nested for loop
A for loop inside another for loop is called nested for loop. Let’s take an example to understand the concept of nested for loop. In this example, we are printing a pattern using nested for loop.
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//outer loop
for(int i=1;i<=6;i++){
//inner loop
for(int j=1;j<=i;j++){
System.out.print("* ");
}
// this is to move the cursor to new line
// to print the next row of the pattern
System.out.println();
}
}
}
Output:

Infinite for loop
A loop that never stops executing is called infinite loop. This happens when the condition expression defined in loop never returns false. The following example will help you understand the importance of Boolean expression and increment/decrement operation co-ordination:
class ForLoopExample2 {
public static void main(String args[]){
for(int i=1; i>=1; i++){
System.out.println("The value of i is: "+i);
}
}
}
This is an infinite loop as the condition would never return false. The initialization step is setting up the value of variable i to 1, since we are incrementing the value of i, it would always be greater than 1 (the Boolean expression: i>1) so it would never return false. This would eventually lead to the infinite loop condition. Thus it is important to see the co-ordination between Boolean expression and increment/decrement operation to determine whether the loop would terminate at some point of time or not.
Here is another example of infinite for loop:
// infinite loop
for ( ; ; ) {
// statement(s)
}
Example: Iterate an array using for loop
Let’s see another example of for loop. Here we are iterating and displaying array elements using the for loop.
class ForLoopExample3 {
public static void main(String args[]){
int arr[]={2,11,45,9};
//i starts with 0 as array index starts with 0 too
for(int i=0; i<arr.length; i++){
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
}
}
Output:
2 11 45 9
Enhanced For loop
Enhanced for loop is another way of defining a loop. This is especially useful when you want to iterate array, ArrayList and other collections classes. Tt is easy to read and write.
Let’s take the same example that we have seen above. We are rewriting it using enhanced for loop.
class ForLoopExample3 {
public static void main(String args[]){
int arr[]={2,11,45,9};
for (int num : arr) {
System.out.println(num);
}
}
}
Output:
2 11 45 9
Note: In the above example, I have declared the num as int in the enhanced for loop. This will change depending on the data type of array. For example, the enhanced for loop for string type would look like this:
String arr[]={"hi","hello","bye"};
for (String str : arr) {
System.out.println(str);
}
Check out these java programming examples related to for loop:
Harsh bhatnagar says
I really appreciate and recommend this website to all the beginners and experienced as well. As i find it very ease in learning java, i’ve been in touch with the same for past 1yr but never been so comfortable with it. But after reading the few tutorials on this website i realized that, my concepts weren’t that much clear which i feel have been cleared after hitting these tutorials.
Thanks –
Sasidhar says
Very Helpful for beginners…As I am from a Non-IT background in my graduation, this site has helped me a lot…Add more sample & simple programs so that we can know more.
Great going guys…keep it up :)
shashi says
I think this array declaration is wrong.it can’t be like this.
int arr[4]={2,11,45,9};
It should be like this
int arr[]={2,11,45,9};
Syed Bilal says
Both ways are correct. He declared and FIXED the size of array to 4 and if I come to your point, you can declare any number of members in your array!. Your concept is good for Multidimensional Array but for Single array.. Always declare the size of array!.
Dragica says
That’s right!
Wuu says
thanks, your comment is helping me a lot.
king says
i think first one was right .
You can right like this :
int [] array = new int[4];
array ={2,11,45,9};
azhar says
I want a real life example. For all the loops can any one help me out
Unknown says
This is one of the best sites for learning java. Concepts are made very clear and explained in such a simple way. Wonderful way of teaching. Thank you so much!