Arraylist class implements List interface and it is based on an Array data structure. It is widely used because of the functionality and flexibility it offers. ArrayList in Java, is a resizable-array implementation of the List interface. It implements all optional list operations and permits all elements, including null. Most of the developers choose Arraylist over Array as it’s a very good alternative of traditional java arrays.
Array vs arraylist in java
The main difference between array and arraylist is that arraylist can grow and shrink dynamically while an array cannot.
An array has a fixed length so if it is full you cannot add any more elements to it. Similarly, if number of elements are removed from ArrayList, the memory consumption remains same as it doesn’t shrink.
On the other hand, ArrayList can dynamically grow and shrink after addition and removal of elements. ArrayList class has several useful methods that can make our task easy.
ArrayList in Java
- ArrayList can grow and shrink automatically based on the addition and removal of elements.
- ArrayList can contain duplicate elements
- ArrayList maintains the insertion order, which means the elements appear in the same order in which they are inserted.
- ArrayList is non synchronized. However you can make it synchronized.
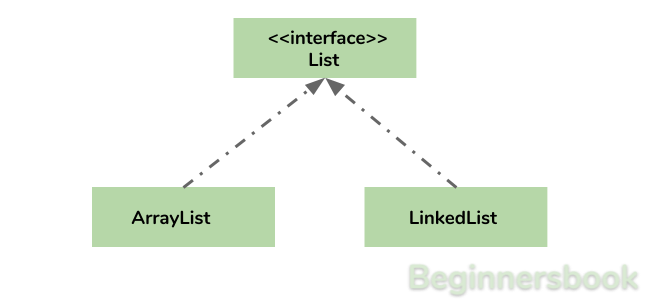
Hierarchy of ArrayList class in Java
ArrayList class implements List interface and List interface extends Collection interface.
Arraylist in Java declaration
This is how you can declare an ArrayList of String type:
ArrayList<String> list=new ArrayList<>();
This is how you can declare an ArrayList of Integer type:
ArrayList<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>();
Adding elements to Arraylist in java
Adding Element in ArrayList at specified position:
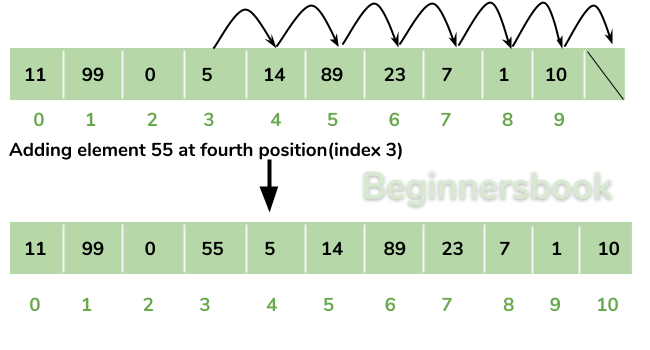
You can add elements to an ArrayList by using add() method. This method has couple of variations, which you can use based on the requirement.
For example: If you want to add the element at the end of the List then you can simply call the add() method like this:
arrList.add("Steve"); //This will add "Steve" at the end of List
To add the element at the specified location in ArrayList, you can specify the index in the add() method like this:
arrList.add(3, "Steve"); //This will add "Steve" at the fourth position
Lets write the complete code:
import java.util.*;
class JavaExample{
public static void main(String args[]){
ArrayList<String> arrList=new ArrayList<String>();
arrList.add("Steve");
arrList.add("Tim");
arrList.add("Lucy");
arrList.add("Pat");
arrList.add("Angela");
arrList.add("Tom");
//displaying elements
System.out.println(arrList);
//Adding "Steve" at the fourth position
arrList.add(3, "Steve");
//displaying elements
System.out.println(arrList);
}
}
Output:
[Steve, Tim, Lucy, Pat, Angela, Tom] [Steve, Tim, Lucy, Steve, Pat, Angela, Tom]
Note: Since the index starts with 0, index 3 would represent fourth position not 3.
Change an element in ArrayList
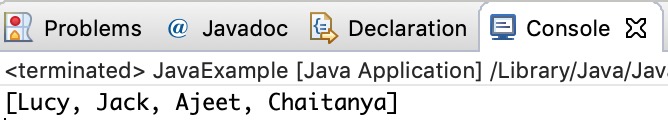
You can use the set method to change an element in ArrayList. You need to provide the index and new element, this method then updates the element present at the given index with the new given element.
In the following example, we have given the index as 0 and new element as “Lucy” in the set() method. The method updated the element present at the index 0 (“Jim”) with the new String element “Lucy”.
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> names = new ArrayList<String>();
names.add("Jim");
names.add("Jack");
names.add("Ajeet");
names.add("Chaitanya");
names.set(0, "Lucy");
System.out.println(names);
}
}
Output:
How to remove element from Arraylist in Java?
Removing Element from ArrayList:
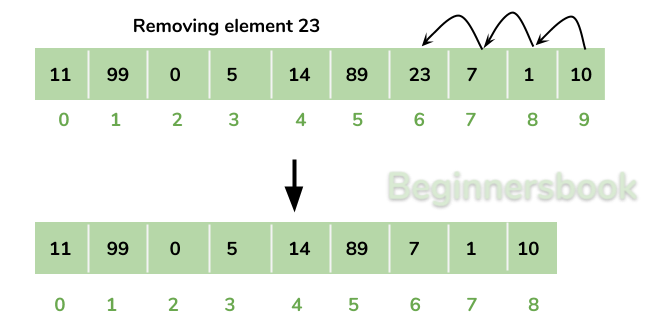
You can use remove() method to remove elements from an ArrayList. Similar to add() method, this method also has couple of variations.
For example:
import java.util.*;
class JavaExample{
public static void main(String args[]){
ArrayList<String> alist=new ArrayList<String>();
alist.add("Steve");
alist.add("Tim");
alist.add("Lucy");
alist.add("Pat");
alist.add("Angela");
alist.add("Tom");
//displaying elements
System.out.println(alist);
//Removing "Steve" and "Angela"
alist.remove("Steve");
alist.remove("Angela");
//displaying elements
System.out.println(alist);
//Removing 3rd element
alist.remove(2);
//displaying elements
System.out.println(alist);
}
}
Output:
[Steve, Tim, Lucy, Pat, Angela, Tom] [Tim, Lucy, Pat, Tom] [Tim, Lucy, Tom]
Iterating ArrayList
Here, we are using enhanced for loop to iterate ArrayList elements. This one of the best ways to iterate an ArrayList of string type.
import java.util.*;
class JavaExample{
public static void main(String args[]){
ArrayList<String> alist=new ArrayList<String>();
alist.add("Gregor Clegane");
alist.add("Khal Drogo");
alist.add("Cersei Lannister");
alist.add("Sandor Clegane");
alist.add("Tyrion Lannister");
//iterating ArrayList
for(String str:alist)
System.out.println(str);
}
}
Output:
Gregor Clegane Khal Drogo Cersei Lannister Sandor Clegane Tyrion Lannister
There are several other ways to loop an ArrayList:
- Using iterator
- Using enhanced for-each loop.
- Using list iterator
- Using for loop
- Using forEachRemaining() method.
ArrayList Size
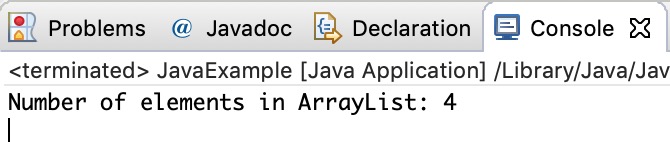
We can use size() method of ArrayList to find the number of elements in an ArrayList.
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> numbers = new ArrayList<Integer>();
numbers.add(1);
numbers.add(7);
numbers.add(5);
numbers.add(6);
System.out.println("Number of elements in ArrayList: "+numbers.size());
}
}
Output:
Sort ArrayList
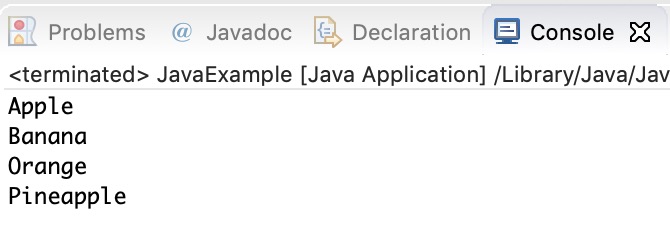
You can use the sort() method of the Collections utility class to sort an ArrayList. This class is is a part of java.util package. In the following example we are sorting a list of String type alphabetically. This method also works on numeric lists (such as Integer type ArrayList).
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> fruits = new ArrayList<String>();
fruits.add("Orange");
fruits.add("Apple");
fruits.add("Banana");
fruits.add("Pineapple");
Collections.sort(fruits);
for (String str : fruits) {
System.out.println(str);
}
}
}
Output:
ArrayList Example in Java
This example demonstrates, how to create, initialize, add and remove elements from ArrayList. In this example we have an ArrayList of “String” type. We are adding 5 String element in the ArrayList using the method add(String E). This method adds the element at the end of the ArrayList.
We are then adding two more elements in the ArrayList using method add(int index, String E). This method adds the specified element at the specified index, index 0 indicates first position, 1 indicates second position and so on.
We are then removing the elements “Chaitanya” and “Harry” from the ArrayList. We again removed the second element of the ArrayList using method remove(int index).
import java.util.*;
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
/* Creating ArrayList of type "String" which means
* we can only add "String" elements
*/
ArrayList<String> obj = new ArrayList<String>();
/*This is how we add elements to an ArrayList*/
obj.add("Ajeet");
obj.add("Harry");
obj.add("Chaitanya");
obj.add("Steve");
obj.add("Anuj");
// Displaying elements
System.out.println("Original ArrayList:");
for(String str:obj)
System.out.println(str);
/* Add element at the given index
* obj.add(0, "Rahul") - Adding element "Rahul" at first position
* obj.add(1, "Justin") - Adding element "Justin" at second position
*/
obj.add(0, "Rahul");
obj.add(1, "Justin");
// Displaying elements
System.out.println("ArrayList after add operation:");
for(String str:obj)
System.out.println(str);
//Remove elements from ArrayList like this
obj.remove("Chaitanya"); //Removes "Chaitanya" from ArrayList
obj.remove("Harry"); //Removes "Harry" from ArrayList
// Displaying elements
System.out.println("ArrayList after remove operation:");
for(String str:obj)
System.out.println(str);
//Remove element from the specified index
obj.remove(1); //Removes Second element from the List
// Displaying elements
System.out.println("Final ArrayList:");
for(String str:obj)
System.out.println(str);
}
}
Output:
Original ArrayList: Ajeet Harry Chaitanya Steve Anuj ArrayList after add operation: Rahul Justin Ajeet Harry Chaitanya Steve Anuj ArrayList after remove operation: Rahul Justin Ajeet Steve Anuj Final ArrayList: Rahul Ajeet Steve Anuj
All methods of Arraylist in Java
In the above examples, we have used methods such as add() and remove(). However there are number of other useful methods available in ArrayList class.
1) add( Object o): This method adds an object o at the end of the arraylist.
obj.add("hello");
This statement would add a string hello in the arraylist at last position.
2) add(int index, Object o): It adds the object o at the specified index in the ArrayList.
obj.add(2, "bye");
It will add the string “bye” at the 2nd index (third element as array list starts with index 0) of array list.
3) remove(Object o): Removes the object o from the ArrayList.
obj.remove("Chaitanya");
This statement will remove the string “Chaitanya” from the ArrayList.
4) remove(int index): Removes element from a given index.
obj.remove(3);
It would remove the element of index 3 (4th element of the list – List starts with o).
5) set(int index, Object o): Used for updating an element. It replaces the element present at the specified index with the object o.
obj.set(2, "Tom");
It would replace the 3rd element (index =2 is 3rd element) with the value Tom.
6) int indexOf(Object o): Gives the index of the object o. If the element is not found in the list then this method returns the value -1.
int pos = obj.indexOf("Tom");
This would give the index (position) of the string Tom in the list.
7) Object get(int index): It returns the object of list which is present at the specified index.
String str= obj.get(2);
This would return the string stored at 3rd position (index 2) and would be assigned to the string “str”. We are using string variable to store the get() result because the list is of string type. If the list is of int type then we can use int variable to store the returned element.
8) int size(): It returns the size of the ArrayList (Number of elements of the list).
int numberofitems = obj.size();
9) boolean contains(Object o): It checks whether the given object o is present in the array list. If the element is found it returns true else it returns false.
obj.contains("Steve");
It would return true if the string “Steve” is present in the list else we would get false.
10) clear(): It is used for removing all the elements of the array list in one go. The below code will remove all the elements of ArrayList whose object is obj.
obj.clear();
Arraylist in Java Interview Questions
These are the popular questions asked during interviews. I have covered them in separate posts as this guide is already long enough and I do not want to make it any longer. Happy learning!
R Pantera says
Thank you very much for your Beginner’s Book. It is better than any other source I have found for a Java beginner. The examples are especially helpful. I wish you success.
Chaitanya Singh says
Thanks for the appreciation. Glad you liked it.
BabaG says
Please how do I get the pdf of your material. Thank a lot
Santosh says
Hi ,
The examples and concepts are explained very nicely and well organized.
Thank you!!
Venkat says
Hi sir! ur way of explanation awesome.this site is best for the java beginners .keep posting…
Rahul Raaj Jamuar says
Thank you so much for posting these contents. The examples given here are best to understand any concept. Keep adding more examples. Thanks again :)
Abel says
Friend,I am not able to Command Array List showing me error: The type ArrayList is not generic; it cannot be parameterized with arguments
Priya says
I suspect you imported some different ArrayList class in your classpath.Try import java.util.ArrayList, and I’m sure it would certainly work. Check your Java version as well, ArrayList is not a legacy class so it might support from JDK 1.5
Priya.
Jai says
Example are clear and easy to understand quickly.
The way of presentation is really very nice.
Thanks ?
TOSYN says
i just stumbled on your website on google, never knew this kind of well explanatory java website exist. Your topics are truly helpful for a java starter(Beginners). i will directed my beginners here.Thanks to you.
veeresh says
Hi, things here are very clear to understand. It is very good for the beginners like me.
Arun Singh says
why can’t we add elements outside of main() method?
sid says
say there are duplicate elements in the list. If I call the method remove(), then will it remove all the duplicate elements?
unu` says
I tried to do this and for example if you have it like this:
If you have the ArrayList created let`s say like this:
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
and you set it like this:
position 0 – “John”
1 – “Michael”
2 – “Mitch”
3 – “Gus”
4 – “John”
5 – “Johnny”
if you say: list.remove(“John”); then it will remove its first occurance.
So, the new elements will be like this:
0 – “Michael”
1 – “Mitch”
2 – “Gus”
3 – “John”
4 – “Johnny”
I hope I was clear enough. :)
prasanth says
The element that was spotted first will be removed with remove() method.The rest of duplicate elements remain in the list.
prasanth says
No.It will not remove all the duplicate elements.remove() method will remove the element specified which occurs at the first instance.
Archana says
it’s really very helpful to understand within less Time..too Good :)
Madhu says
It helped me a lot …concepts are very clear
David says
So glad i came here, please do you have learning Java as a whole in PDF format?
Hans Raj says
I want to compare arraylist with my string input in if statement. if condition becomes true then it return me the element or string which i compared in if statement.
Please help.
thanks in advance
nivedita says
how to create customized collection that accepts only positive numbers as input
vedavathi J Reddy says
No words to say, That much your tutorials are impressing. i can get everything in single website, which is very great thing.
its really helpfull to add spring and hibernate with this page.
Santosh says
Nice concept explanation step by step.
pics cua says
wow thanks very much. It’s really helpful. So how can i access it in pdf
shanthi says
is there any method that removes all elements matching the given element(including duplicates)in collection framework.
please advise.
Emad Beltaje says
Thank you very very very much..for sharing ur knowledge with us with great style
#Respect_From_Palestine <3
DHARMENDHAR says
Such A Lovely Explanations , i had suggested all my friends for Beginnerbooks.com
Thank you Team.
God Bless You
MRC says
May I add an element in a single line? Is possible
M Ravichandran says
How to add number elements in a single line of code?
Mayur Kandalkar says
amazing explanation!
Kokila Viswanathan says
Really really very very good tutorial for beginners..Please read this tutorial if any one want to know clear idea about collections…After reading this tutorial 90% of ideas you can get in collections and am damn sure..
Anold says
Where can i find Java array of Objects, help me please
Carlos Mercado says
Good job. Thanks for the help from Argentina!
Shalala says
This is really awasome site for who want to learn better. Thank you for creating this site.
Noah Moud says
Really cool,, thank you!
Are you planning on adding JavaScript to your languages?
Himanshu Gangwar says
Very helpful thanks. A crores of time sir