Try with resource statement was first introduced in Java 7. This statement has received a major enhancement in Java 9. In this guide, we will discuss the improvements of try-with-resource statement in Java 9.
What is Try-With-Resources?
This statement was first introduced in Java 7 to avoid the redundant code that we had to write for exception handling. The advantages of this statement are:
1. Try with resources closes all the resources (file, database connection, network connection etc.) automatically. No need to close them explicitly. This prevents memory leaks.
2. With the help of try with resource we can reduce the unnecessary lines of code and makes the code more readable.
How we used to write the code in Java 7 using Try-With-Resources?
This is how we use the Try-With-Resource statement in Java 7.
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
try(FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("beginnersbook.txt");){
//We are writing this string in the output file using FileOutputStream
String mystring = "We are writing this line in the output file.";
//Converting the given string in bytes
byte bytes[] = mystring.getBytes();
//Writing the bytes into the file
fileOutputStream.write(bytes);
//Displaying success message after the successful write operation
System.out.println("The given String is written in the file successfully");
}catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
Output:
The given String is written in the file successfully
Problem with the Try-With-Resources in Java 7
There were certain issues with the Try-With-Resource statement in Java 7. This statement didn’t allow the resources to be declared outside of the statement block (scope). Lets take an example to understand this.
Java 7 – Resource declared outside the Try-With-Resources block
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("beginnersbook.txt");
try(fileOutputStream){
String mystring = "We are writing this line in the output file.";
byte bytes[] = mystring.getBytes();
fileOutputStream.write(bytes);
System.out.println("The given String is written in the file successfully");
}catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
Output in Java 7:
Compile-time error
The above example throws compile-time error because the resource is declared outside the scope of Try-With-Resource statement.
Java 7 – Resource declared outside – duplicate resource as workaround
To solve the above error, we had to do a workaround in Java 7. We used to duplicate the resource reference like this:
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("beginnersbook.txt");
try(FileOutputStream fileOutputStream2 = fileOutputStream){
String mystring = "We are writing this line in the output file.";
byte bytes[] = mystring.getBytes();
fileOutputStream2.write(bytes);
System.out.println("The given String is written in the file successfully");
}catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
This code would run fine in Java 7.
Note the FileOutputStream fileOutputStream2 = fileOutputStream line in the try block. We created another reference to the already declared output stream within the scope of Try-With-Resource.
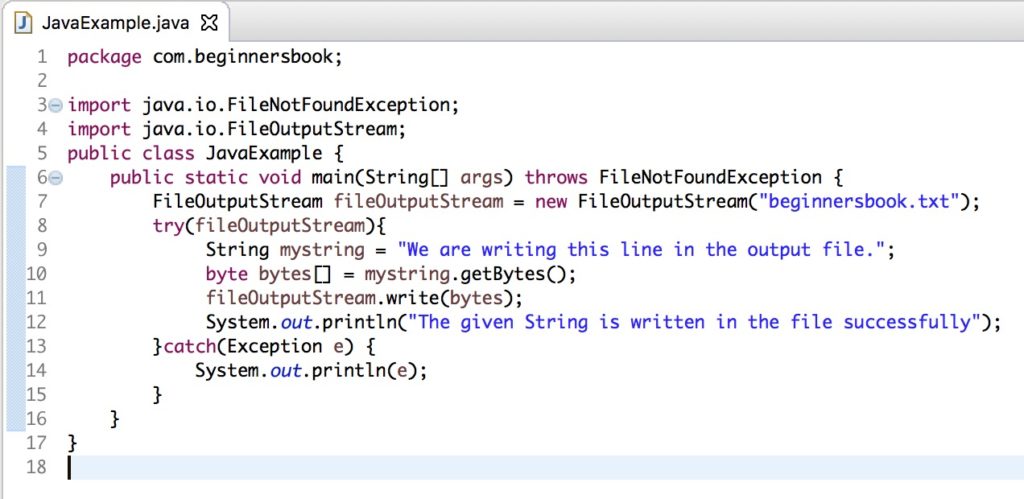
Java 9 – Try-With-Resources Enhancements
Java 9 provided a major enhancement to the traditional Try-With-Resource statement. Java 9 allows us to declare the resource outside of the Try-With-Resource block. We no longer need to create the local variable to access the resource. Lets take the same example that we have taken in Java 7 but got a compilation error. In Java 9, this code runs perfectly fine.
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("beginnersbook.txt");
try(fileOutputStream){
String mystring = "We are writing this line in the output file.";
byte bytes[] = mystring.getBytes();
fileOutputStream.write(bytes);
System.out.println("The given String is written in the file successfully");
}catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
Output:
The given String is written in the file successfully
Screenshot of this code in Eclipse Oxygen running Java SE 9.
Leave a Reply