In this guide, you will learn about string array in java, how to use them and various operations that you can perform on string array in java.
String array is a collection of strings, stored in contiguous memory locations.
For example: The following string array contains four elements. These elements are stored in contiguous memory locations and can be accessed using array index such as: names[0] represents first element "Chaitanya". Similarly names[1] represents second element "Ajeet", names[2] represents third element "Hari” and so on.
String[] names = new String[] {"Chaitanya", "Ajeet", "Hari", "Rahul"};
String Array Declaration
There are two ways to declare a String array in Java.
1. Without specifying the array size:
String[] strArray;
2. Array size is specified: The following array can hold upto 5 strings.
String[] strArray = new String[5];
String Array Initialization
1. Inline Initialization:
String[] names = new String[] {"Chaitanya", "Ajeet", "Hari", "Rahul"};
OR
String[] names = {"Chaitanya", "Ajeet", "Hari", "Rahul"};
2. Normal Initialization after declaration:
Here, we have declared an array names with the fixed size of 4 and initialized the array later.
String[] names= new String[4]; names[0]= "Chaitanya"; //first element names[1]= "Ajeet"; //second element names[2]= "Hari"; //third element names[3]= "Rahul"; //last element
Simple String Array Example in Java
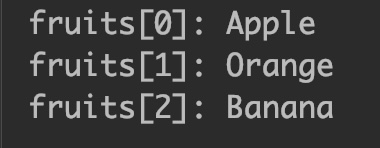
In this example, we have a string array fruits. This array contains three elements (strings). We are displaying the elements of string array using for loop. The length property of array (fruits.length) returns the number of elements in an array, in this case its 3.
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String a[]){
//declared and initialized a string array
String[] fruits = new String[]{"Apple", "Orange", "Banana"};
for (int i=0; i<fruits.length; i++)
{
System.out.println("fruits["+i+"]: "+fruits[i]);
}
}
}
Output:
String array ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
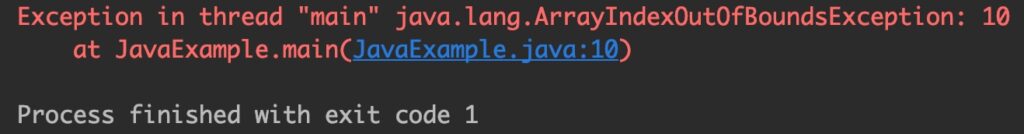
If the specified index is beyond the size of the array then the compiler throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException.
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String a[]){
//declared and initialized a string array
String[] fruits = new String[]{"Apple", "Orange", "Banana"};
//We are trying to print 11th element of the array
//but the array contains only 3 elements. This will
//throw ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
System.out.println(fruits[10]);
}
}
Output:
Iterating a String Array
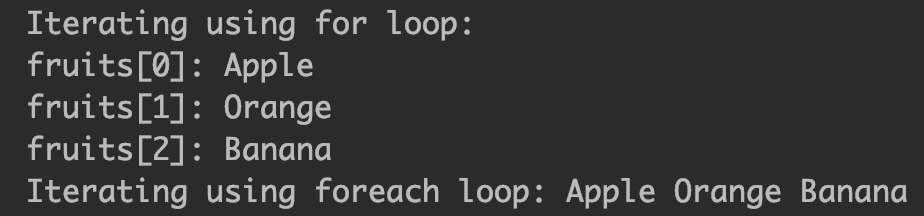
Let’s see how to iterate a string array. We can iterate using normal for loop or enhanced for loop (for each loop).
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String a[]){
//declared and initialized a string array
String[] fruits = new String[]{"Apple", "Orange", "Banana"};
//iterating using normal for loop
System.out.println("Iterating using for loop:");
for (int i=0; i<fruits.length; i++)
{
System.out.println("fruits["+i+"]: "+fruits[i]);
}
//iterating using for-each loop
System.out.print("Iterating using foreach loop: ");
for (String str: fruits)
{
System.out.print(str+ " ");
}
}
}
Output:
Adding elements to String array
You already learned that the size of the array is fixed, which means if it is full, you cannot add any more elements to it. However there are two ways, you can add elements to an array. Technically it’s not adding the elements to the existing array, rather a new array with all the elements of previous array along with the new elements.
1. Creating a new array
2. Using ArrayList
1. Adding elements to an array by creating new array
Steps followed in this program are:
1. Create a new array with the larger size to accommodate new elements.
2. Copy all elements from old array to new array.
3. Add new elements to new array.
4. Print new array
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String a[]){
//declared and initialized a string array
String[] fruits = new String[]{"Apple", "Orange", "Banana"};
//we want to add two more elements to the fruits array so let's
//create a new array with the size of 5
String[] newFruits = new String[fruits.length+2];
//copying elements from old array to new array
for (int i=0; i<fruits.length; i++)
{
newFruits[i] = fruits[i];
}
//Adding new elements
newFruits[newFruits.length-2]= "Mango"; //second last element
newFruits[newFruits.length-1]= "Kiwi"; //last element
//print new array
for (String str: newFruits)
{
System.out.println(str);
}
}
}
Output:
Apple Orange Banana Mango Kiwi
2. Adding elements to an array using ArrayList
Steps followed in this program are:
1. Convert array to ArrayList.
2. Add as many elements as you like in ArrayList as ArrayList is dynamic and can grow and shrink automatically.
3. Once addition is done, convert back the ArrayList to an Array.
4. Print the array.
import java.util.*;
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String a[]){
//declared and initialized a string array
String[] fruits = new String[]{"Apple", "Orange", "Banana"};
//Convert the array "fruits" to an ArrayList
ArrayList<String> fruitList =
new ArrayList<String>(Arrays.asList(fruits));
//Adding elements to ArrayList
fruitList.add("Mango");
fruitList.add("Kiwi");
//Convert the ArrayList to array
String[] newFruits = fruitList.toArray(new String[fruitList.size()]);
//print new array
for (String str: newFruits)
{
System.out.println(str);
}
}
}
Output:
Apple Orange Banana Mango Kiwi
Sorting string array
Here, we are demonstrating how to sort a string array. It is simple, just import java.util.Arrays package to use the sort() method of Arrays class. The array passed in the sort() method is sorted in ascending order.
import java.util.Arrays;
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String a[]){
String[] names = new String[]{"Chaitanya", "Steve", "Rob", "Ajeet"};
//print array before sorting
System.out.println("Array before sorting: ");
for (String str: names)
{
System.out.print(str+ " ");
}
//sorting array
Arrays.sort(names);
//new line
System.out.println();
//print array after sorting
System.out.println("Array after sorting: ");
for (String str: names)
{
System.out.print(str+ " ");
}
}
}
Output:

Search an element in a String array
Here, we are searching an element in string array. We are iterating the whole array and matching every element with the searchItem, if a match is found, we are storing the index and setting the foundFlag to true. If the whole array is traversed and no match is found then the if-else statement after for loop, prints the message that “String is not found”.
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String a[]){
String[] names = new String[]{"Chaitanya", "Steve", "Rob", "Ajeet"};
//this will represent the index of search element when it is found
int index=0;
//This will set to true, if element is found in array, else it
//will remain false.
boolean foundFlag = false;
//This is the search element, we are searching for this element in array
String searchItem ="Rob";
for (int i = 0; i < names.length; i++) {
if(searchItem.equals(names[i])) {
//if element found, get index, set flag to true and break the loop
index = i;
foundFlag = true;
break;
}
}
if(foundFlag)
System.out.println("String "+searchItem +" is found at index: "+index);
else
System.out.println("String "+searchItem +" is not found");
}
}
Output:
String Rob is found at index: 2