When a class extends a class, which extends anther class then this is called multilevel inheritance. For example class C extends class B and class B extends class A then this type of inheritance is known as multilevel inheritance.
Lets see this in a diagram:
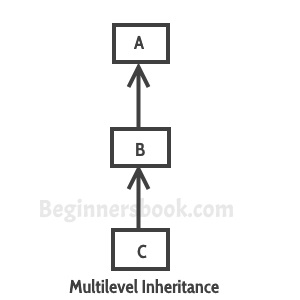
It’s pretty clear with the diagram that in Multilevel inheritance there is a concept of grand parent class. If we take the example of this diagram, then class C inherits class B and class B inherits class A which means B is a parent class of C and A is a parent class of B. So in this case class C is implicitly inheriting the properties and methods of class A along with class B that’s what is called multilevel inheritance.
To learn the basics of inheritance refer this tutorial: Inheritance in Java
Multilevel Inheritance Example
In this example we have three classes – Car, Maruti and Maruti800. We have done a setup – class Maruti extends Car and class Maruti800 extends Maruti. With the help of this Multilevel hierarchy setup our Maruti800 class is able to use the methods of both the classes (Car and Maruti).
class Car{
public Car()
{
System.out.println("Class Car");
}
public void vehicleType()
{
System.out.println("Vehicle Type: Car");
}
}
class Maruti extends Car{
public Maruti()
{
System.out.println("Class Maruti");
}
public void brand()
{
System.out.println("Brand: Maruti");
}
public void speed()
{
System.out.println("Max: 90Kmph");
}
}
public class Maruti800 extends Maruti{
public Maruti800()
{
System.out.println("Maruti Model: 800");
}
public void speed()
{
System.out.println("Max: 80Kmph");
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Maruti800 obj=new Maruti800();
obj.vehicleType();
obj.brand();
obj.speed();
}
}
Output:
Class Car Class Maruti Maruti Model: 800 Vehicle Type: Car Brand: Maruti Max: 80Kmph
Mohammad says
Your explanation was very helpful for me
Thanks a lot..
bhargav says
i want details of an employee working in company like his name ,age ,designation by typing his name i want to get all details of him by using multiple inheritance in java? please provide this answer?