Java String format() method is used for formatting the String. It works similar to printf function of C, you can format strings using format specifiers.
There are so many things you can do with this method, for example you can concatenate the strings using this method and, at the same time you can format the output of concatenated string. In this tutorial, we will see several examples of Java String format() method.
Syntax of format() method
String formattedString = String.format(String format, Object... args);
Common Format Specifiers
%s– String%d– Integer%f– Floating point number%t– Date/Time%x– Hexadecimal
Java String format() method Examples
1. Formatting Strings:
The format specifier %s is replaced by the value of variable name in the output.
public class Example{
public static void main(String args[]){
String name = "Chaitanya";
String message = String.format("Hello, %s!", name);
System.out.println(message);
// Output: Hello, Chaitanya!
}
}
2. Formatting Numbers:
This example is similar to the above example, here we are formatting numbers in the output string. Format specifier %d is used for numbers.
public class Example{
public static void main(String args[]){
int myAge = 37;
String formattedAge = String.format("My Age is: %d", myAge);
System.out.println(formattedAge);
// Output: My Age is: 37
}
}
3. Formatting Floating Point Numbers
public class Example{
public static void main(String args[]){
double num = 456.789;
String formattedNum = String.format("Number: %.2f", num);
System.out.println(formattedNum);
// Output: Number: 456.789
}
}
4. Formatting Different Types
public class Example{
public static void main(String args[]){
String name = "Chaitanya";
int age = 37;
double luckyNum = 123.456;
String formattedString = String.format("Name: %s, Age: %d, Lucky No: $%.2f", name, age, luckyNum);
System.out.println(formattedString);
// Output: Name: Chaitanya, Age: 37, Lucky No: $123.456
}
}
5. Formatting Dates
import java.util.Date;
public class Example{
public static void main(String args[]){
Date date = new Date();
String formattedDate = String.format("Current DateTime: %tc", date);
System.out.println(formattedDate);
// Output: Current DateTime: Sat Jun 08 07:39:52 PDT 2024
}
}
6. Padding and Aligning
public class Example{
public static void main(String args[]){
String leftAligned = String.format("|%-10s|", "left");
String rightAligned = String.format("|%10s|", "right");
System.out.println(leftAligned);
System.out.println(rightAligned);
// Output:
// |left |
// | right|
}
}
7. Format Flags
-: Left-justify within the given field width; right justification is the default.+: Include a sign (+ or -) with numeric values.0: Pad with zeroes (0) instead of spaces.
public class Example{
public static void main(String args[]){
int number = 123;
String formattedNumber = String.format("%+08d", number);
System.out.println(formattedNumber);
// Output: +0000123
}
}
8. Concatenating arguments to the string
We can specify the argument positions using %1$, %2$,..format specifiers. Here %1$ represents first argument, %2$ second argument and so on.
public class Example{
public static void main(String args[]){
String str1 = "cool string";
String str2 = "88";
/* Specifying argument positions. %1$ is for the first argument and
* %2$ is for the second argument
*/
String fstr = String.format("My String is: %1$s, %1$s and %2$s", str1, str2);
System.out.println(fstr);
//output: My String is: cool string, cool string and 88
}
}
As you can see that how we have passed the string “cool string” twice in the format() method using the argument positions format specifiers.
9. Left padding the string using string format()
In this example, we are left padding a number with 0’s and converting the number to a formatted String. In the above example we have formatted the float numbers and Strings and in this example we are formatting an integer. The important point to remember is that the format specifiers for these are different.
%s – for strings
%f – for floats
%d – for integers
public class Example{
public static void main(String args[]){
int str = 88;
/* Left padding an integer number with 0's and converting it
* into a String using Java String format() method.
*/
String formattedString = String.format("%05d", str);
System.out.println(formattedString);
}
}
Output:
00088
Displaying Different types of values using String format() method
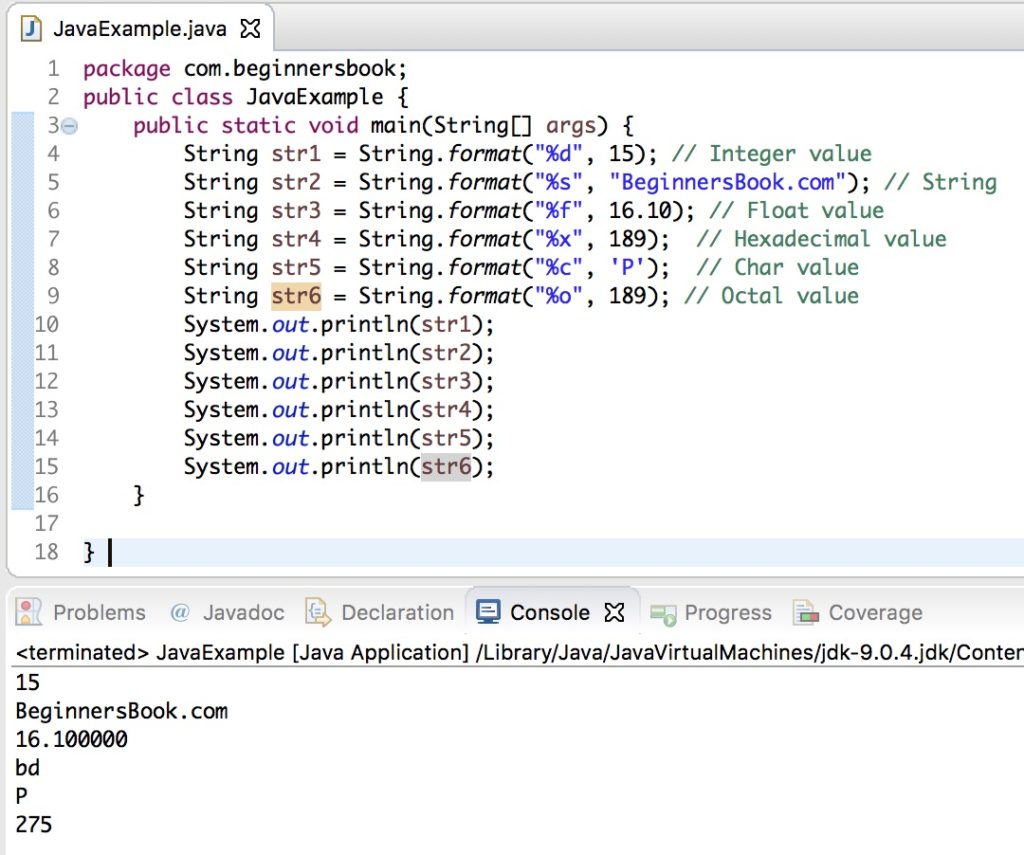
In the following example, we are using different format specifiers to display values of different types. Here we have shown few examples of how an integer value can be converted into an octal or hexadecimal value using format() method. After this example, we have shared a list of available format specifiers.
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = String.format("%d", 15); // Integer value
String str2 = String.format("%s", "BeginnersBook.com"); // String
String str3 = String.format("%f", 16.10); // Float value
String str4 = String.format("%x", 189); // Hexadecimal value
String str5 = String.format("%c", 'P'); // Char value
String str6 = String.format("%o", 189); // Octal value
System.out.println(str1);
System.out.println(str2);
System.out.println(str3);
System.out.println(str4);
System.out.println(str5);
System.out.println(str6);
}
}
Output:
Leave a Reply