Java 7 introduced the @SafeVarargs annotation to suppress the unsafe operation warnings that arises when a method is having varargs (variable number of arguments). The @SafeVarargs annotation can only be used with methods (final or static methods or constructors) that cannot be overriden because an overriding method can still perform unsafe operation on their varargs (variable number of arguments).
Java 9 extended the use of @SafeVarargs annotation, it can now used with private methods as well. This is because private methods cannot be overridden. Earlier this annotation was limited to the final or static methods, or constructors but now it can be used with private methods.
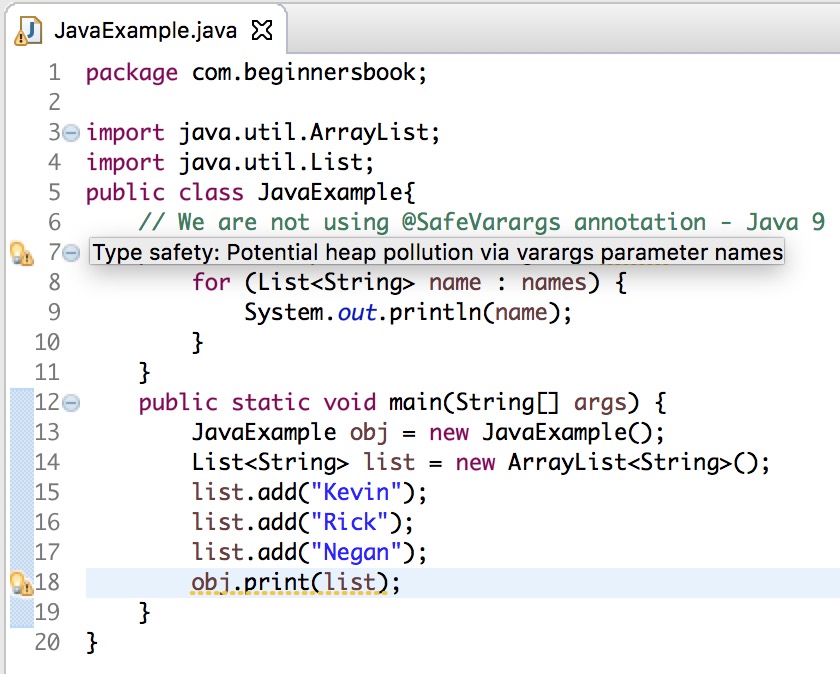
Java 9 Example – When we do not use @SafeVarargs annotation?
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class JavaExample{
// We are not using @SafeVarargs annotation - Java 9
private void print(List... names) {
for (List<String> name : names) {
System.out.println(name);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
JavaExample obj = new JavaExample();
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
list.add("Kevin");
list.add("Rick");
list.add("Negan");
obj.print(list);
}
}
Warnings:
Type safety: Potential heap pollution via varargs parameter names Type safety: A generic array of List is created for a varargs parameter
Output:
[Kevin, Rick, Negan]
As you can see the code ran fine but it produced few warnings.
Screenshot of this code in Eclipse Oxygen IDE showing the warnings.
Java 9 – @SafeVarargs Annotation Example
Lets run the same code again after using the @SafeVarargs annotation.
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class JavaExample{
@SafeVarargs
private void print(List... names) {
for (List<String> name : names) {
System.out.println(name);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
JavaExample obj = new JavaExample();
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
list.add("Kevin");
list.add("Rick");
list.add("Negan");
obj.print(list);
}
}
The same output without any warnings.
Note: If you try to compile the above code in Java 7 and Java 8, you will get a compilation error because this enhancements is done in Java 9, prior to java 9 – private methods are not allowed to be marked with this annotation.
Leave a Reply