When working with method overloading, sometimes we encounter compile time error “reference is ambiguous”. This error usually occurs when we pass null value while calling overloaded methods. In this guide, we will see few examples to see when this error occurs and how to avoid it.
Prerequisite: Method Overloading in Java
Method Overloading reference is ambiguous error
Let’s see the following program where this error occurs and then we will discuss why this error occurs and how to avoid it.
public class JavaExample
{
// Overloaded methods
public void printParam(Integer i)
{
System.out.println("Int: "+i);
}
public void printParam(String str)
{
System.out.println("String: "+str);
}
// Main method
public static void main(String [] args)
{
JavaExample obj = new JavaExample();
// This will throw compilation error
obj.printParam(null);
}
}
Output:
![]()
In the above example, we have overloaded a method printParam(), one variation of this method accepts Integer values as parameter and other variation accepts String values as parameter.
The reason why we got the error in above program is that the compilation got confused when we passed null value while calling the printParam() method as both Integer and String are not primitive data types, they both accept null values. Compiler is not sure which variation of printParam() method, it should call, thus this error is thrown.
How to avoid error while passing null values to Overloaded methods
Let’s modify the above code like this:
public class JavaExample
{
// Overloaded methods
public void printParam(Integer i)
{
System.out.println("Int: "+i);
}
public void printParam(String str)
{
System.out.println("String: "+str);
}
// Main method
public static void main(String [] args)
{
JavaExample obj = new JavaExample();
String s = null;
// This will not throw an error as it will call String param variation
obj.printParam(s);
}
}
Output:
String: null
Here we are not getting any error as we specified the type of null value that we are passing to the printParam() method while calling it. The compiler is not confused in this case as it would call the String param variation of this method.
Another example of Method overloading for null Argument
public class JavaExample
{
// Overloaded methods
public void printParam(Integer i)
{
System.out.println("Int: "+i);
}
public void printParam(String str)
{
System.out.println("String: "+str);
}
public void printParam(Object obj)
{
System.out.println("Object called");
}
public void printParam(char[] ch)
{
System.out.println("Char Array called");
}
// Main method
public static void main(String [] args)
{
JavaExample obj = new JavaExample();
// This will throw error
obj.printParam(null);
}
}
Solution: Lets specify the type of null values while calling the overloaded methods.
public class JavaExample
{
// Overloaded methods
public void printParam(Integer i)
{
System.out.println("Int: "+i);
}
public void printParam(String str)
{
System.out.println("String: "+str);
}
public void printParam(Object obj)
{
System.out.println("Object called");
}
public void printParam(char[] ch)
{
System.out.println("Char Array called");
}
// Main method
public static void main(String [] args)
{
JavaExample obj = new JavaExample();
//You can call specific overloading method while passing null values
//like this
obj.printParam((char[])null);
obj.printParam((String)null);
obj.printParam((Integer)null);
obj.printParam((Object)null);
}
}
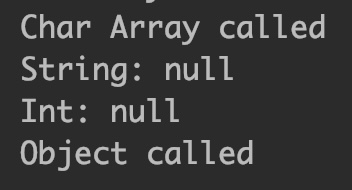
Output: