The split() method of Pattern class is used to split a string based on the specified pattern. Similar to java string split method, this method also accepts regular expression as delimiter.
The Pattern class belongs to java.util.regex package, you need to import java.util.regex.Pattern package to use this class.
There are two variants of the Java Pattern split() method:
- String[] split(CharSequence p): It breaks the string based on the specified pattern p, It returns all a string array that contains all the substring produced after split.
- String[] split(CharSequence p, int limit): This limits the number of substrings produced by pattern split() method. Unlike the first variant that returns all the substrings, it only returns the limited substrings specified by the limit argument.
Example 1: Pattern.split() when no limit is defined
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//delimiter dot(.) is specified as pattern
//Use the double backslash before dot as escape sequence
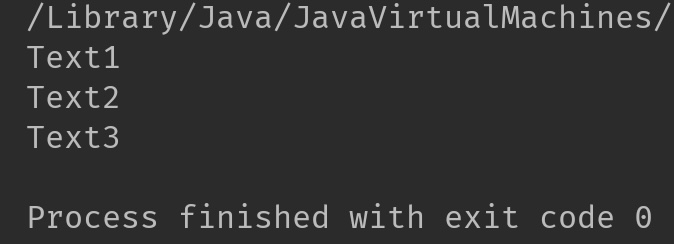
Pattern p = Pattern.compile("\\.");
String[] strArray = p.split("Text1.Text2.Text3");
for(String s:strArray)
{
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
Output:
Example 2: Pattern.split() with limit
Here, we are specifying the limit in the split() method. This will restrict the number of substrings returned from this method.
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
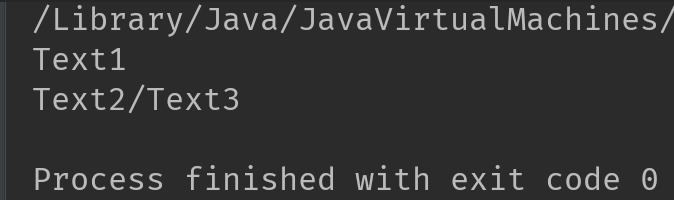
Pattern p = Pattern.compile("/");
//limit is specified as 2
String[] strArray = p.split("Text1/Text2/Text3", 2);
for(String s:strArray)
{
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
Output: As you can see, only two substrings are returned after split because the limit argument is 2.