The substring() method is used to get a substring from a given string. This is a built-in method of string class, it returns the substring based on the index values passed to this method. For example: “Beginnersbook”.substring(9) would return “book” as a substring.
This method has two variants, one is where you just specify the start index and in the other variant, you can specify both start and end indexes.
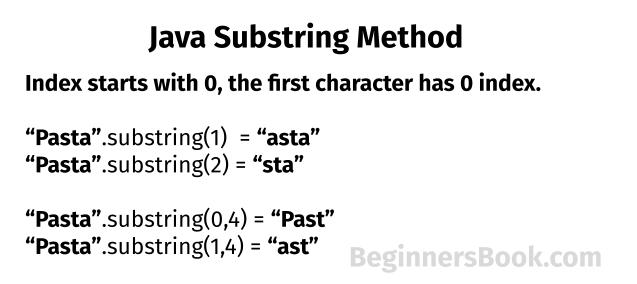
String substring() method variants
There are two variants of substring method in Java.
1. Only the beginIndex:
String substring(int beginIndex)
Returns the substring starting from the specified index beginIndex till the last character of the string.
For example: "Chaitanya".substring(2) would return "aitanya". The beginIndex is inclusive, that is why the character present at the index 2 is included in the substring.
This method throws IndexOutOfBoundsException If the beginIndex is less than zero or greater than the length of String (beginIndex<0||> length of String).
2. Both beginIndex and endIndex:
String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex)
Returns a substring starting from specified beginIndex till the character present at endIndex – 1. Thus the length of the substring is endIndex-beginIndex. In other words you can say that beginIndex is inclusive and endIndex is exclusive while getting the substring.
For example: "Chaitanya".substring(2,5) would return "ait".
It throws IndexOutOfBoundsException If the beginIndex is less than zero OR beginIndex > endIndex OR endIndex is greater than the length of String.
Java String substring() examples
Now that we understand the basics of substring() method, let’s take few examples to understand the usage of this method.
1. Basic substring example demonstrates both the variants of this method
Before we start to see some interesting substring method examples, let’s start with a simple example that demonstrates the usage of this method.
public class JavaExample{
public static void main(String args[]) {
String str= new String("WelcomeHome!");
System.out.print("Substring starting from index 7: ");
System.out.println(str.substring(7));
System.out.print("Substring from beginIndex 3 till endIndex 7: ");
System.out.println(str.substring(3, 7));
}
}
Output:

Note: The returned substring length is always endIndex-beginIndex, In our example beginIndex is 3 and endIndex is 7, thus the length of returned substring should be 7-3 = 4.
2. Get a substring between two delimiters
In this program, we are using indexOf() and substring() method of Java String class.
We are finding the indexes of delimiters in the string using indexOf() method. Once we have the indexes of delimiters, we are calling substring method to find the substring between these delimiters.
Note: The method is called like this: substring(start + 1, end), here start index is +1 because, we want to get the substring after the delimiter position, however the end index is not +1 because end index is not inclusive in substring method.
public class JavaExample{
public static void main(String[] args){
//given string
String str = "Welcome to [BeginnersBook.com]";
//we would like to get the substring between '[' and ']'
int start = str.indexOf("[");
int end = str.indexOf("]");
String outStr = str.substring(start + 1, end);
System.out.println(outStr);
}
}
Output:
BeginnersBook.com
Similarly you can use the same logic to get the substring between two characters:
public class JavaExample{
public static void main(String[] args){
//input string
String str = "abcdefg";
//get the substring between two characters 'a' 'd'
int start = str.indexOf('a');
int end = str.lastIndexOf('d');
String outStr = str.substring(start+1, end);
System.out.println(outStr);
}
}
Output:
bc
3. Get a substring between two given strings
This is another interesting example. Here we have a string and we want to get a substring between two strings “Beginners” and “com”. To do this, we have searched the index of first string using indexOf() and added the length of this string, this is because indexOf() gives the index of first character of the string but we want to start reading after the end of string “Beginners”.
Similarly, we found the starting index of second string “com” and get the substring between these indexes using substring method.
public class JavaExample{
public static void main(String[] args){
//input string
String str = "Welcome to [BeginnersBook.com]";
//get the substring between "Beginners" and "com"
int start = str.indexOf("Beginners")+"Beginners".length();
int end = str.lastIndexOf("com");
String outStr = str.substring(start, end);
System.out.println(outStr);
}
}
Output:
Book.
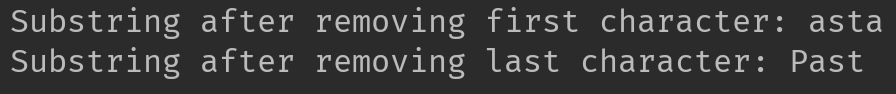
4. Remove first and last character from a string
In this program, we are using substring() method to exclude first and last character from the string.
- str.substring(1): This excludes first character as the index 0 character (first character) is excluded.
- substring(0, str.length()-1): This excludes last character as the length() method returns the length of the string and when we provide
str.length()-1as the endIndex, it excludes last character.
public class JavaExample{
public static void main(String args[]) {
String str= new String("Pasta");
System.out.print("Substring after removing first character: ");
System.out.println(str.substring(1));
System.out.print("Substring after removing last character: ");
System.out.println(str.substring(0, str.length()-1));
}
}
Output:
David says
I think the second result is “jumps”
Laila says
I thought it would be ” jump” if we consider the space before the word “jumps” as a character.
As its explained above the example , “chaitanya”.substring(2,5) and the result is “a(2)i(3)t(4)”, so the fifth character isn’t taken ?
Rana Imran says
also count space ,secondly 20 end at “s”,so java show less one character.so result is jump.
Example:
abc
012
(0,1) show just a exclusive end point.
Cyril says
No it’s correct the result is ” jump” with a space before
Anony-mouse says
When using .substring(x,y), the x index is inclusive and y index is exclusive, therefore it is “jump”.
Abhinabo says
had forgotten the concept
the example helped alot, thanks!
pyguillemet says
To sum up :
– O base index
– Range [beginIndex, endIndex[
– Ex: “abc 123”.substring(1,5) => “bc 1”
vijayasree says
Hello…Good example,it counts the spaces too and gives the result.
HA says
may want to review the java documentation (the key here is how the end index is handled: as value-1, or in other words “exclusively”):
public String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex)
Returns a new string that is a substring of this string. The substring begins at the specified beginIndex and extends to the character at index endIndex – 1. Thus the length of the substring is endIndex-beginIndex.
Examples:
“hamburger”.substring(4, 8) returns “urge”
“smiles”.substring(1, 5) returns “mile”
Parameters:
beginIndex – the beginning index, inclusive.
endIndex – the ending index, exclusive.
Returns:
the specified substring.
Throws:
IndexOutOfBoundsException – if the beginIndex is negative, or endIndex is larger than the length of this String object, or beginIndex is larger than endIndex.
see: https://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/api/java/lang/String.html#substring(int,%20int)
ejthayer says
Most computer languages for many years used a start index and a length as the parameters. For some reason Java decided to use a start and end index that actually returns the characters from start to end – 1. Personally I think this is a horrible implementation of this command, seems like a massive brain stress by the creators of Java. Now that Java is so popular there are 2 major ways this function works now that this stupid implementation has been repeated in several other languages.
Khushi Mehrotra says
Good helped a lot