Java Math.cos() method returns the trigonometric cosine of the given angle in radians. This angle value is passed as an argument to this method and it returns the cosine value ranging from -1 to 1. For example, Math.cos(Math.toRadians(0)) returns 1.0.
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double degrees = 0;
//conversion degree to radians
double radians = Math.toRadians(degrees);
System.out.println(Math.cos(radians));
}
}
Output:
1.0
Syntax of Math.cos() method
Math.cos(Math.toRadians(180)); //returns -1.0
cos() Description
public static double cos(double a): Returns trigonometric cosine value of the given angle a.
cos() Parameters
- a: The double type argument in radians.
cos() Return Value
- Returns cosine of the argument.
- If the argument is NaN or infinity, then it returns NaN.
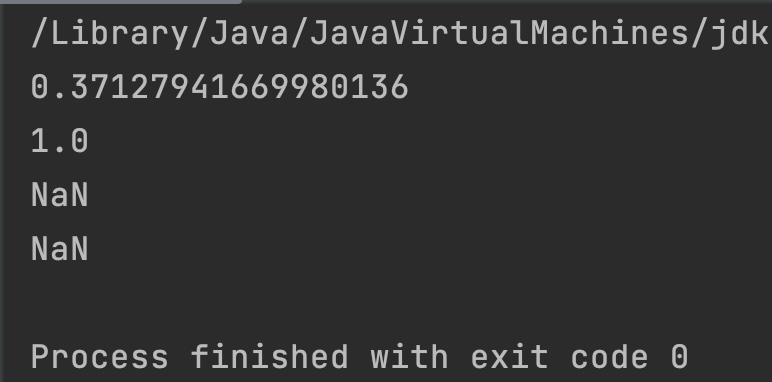
Example 1
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double degrees = 0;
double degrees2 = 90;
double degrees3 = 180;
double degrees4 = 270;
System.out.println(Math.cos(Math.toRadians(degrees)));
System.out.println(Math.cos(Math.toRadians(degrees2)));
System.out.println(Math.cos(Math.toRadians(degrees3)));
System.out.println(Math.cos(Math.toRadians(degrees4)));
}
}
Output:

Example 2
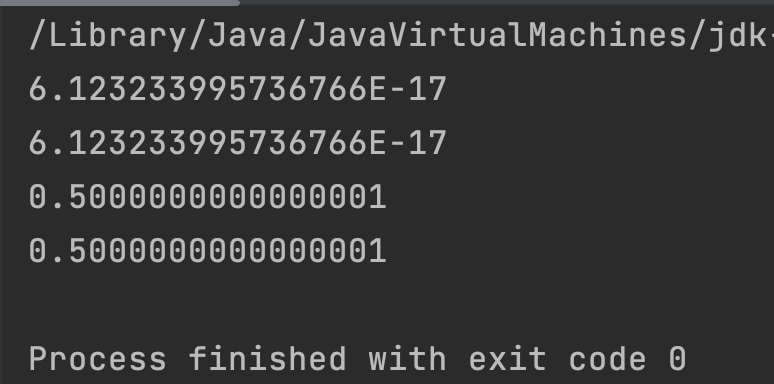
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double degrees = 90;
double degrees2 = -90;
double degrees3 = 60;
double degrees4 = -60;
System.out.println(Math.cos(Math.toRadians(degrees)));
System.out.println(Math.cos(Math.toRadians(degrees2)));
System.out.println(Math.cos(Math.toRadians(degrees3)));
System.out.println(Math.cos(Math.toRadians(degrees4)));
}
}
Output:
Example 3
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double degrees = Double.MAX_VALUE;
double degrees2 = Double.MIN_VALUE;
double degrees3 = 0.0/0; //NaN
double degrees4 = 10.0/0; //Infinity
System.out.println(Math.cos(Math.toRadians(degrees)));
System.out.println(Math.cos(Math.toRadians(degrees2)));
System.out.println(Math.cos(Math.toRadians(degrees3)));
System.out.println(Math.cos(Math.toRadians(degrees4)));
}
}
Output: