Java Math.nextAfter() method returns the floating point number adjacent to the first argument, in the direction of second argument.
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double d1 = 12.8; //used for magnitude
double d2 = 15; //used for direction
double d3 = 10; //another direction
System.out.println(Math.nextAfter(d1, d2));
System.out.println(Math.nextAfter(d1, d3));
}
}
Output:
12.800000000000002 12.799999999999999
Syntax of Math.nextAfter() method
Math.nextAfter(1, 2); //returns 1.0000001
nextAfter() Description
public static double nextAfter(double num, double direction): It returns the floating point number adjacent to the first argument num, in the direction of second argument direction. Another variation of this method is:
public static float nextAfter(float num, double direction)
nextAfter() Parameters
- num: Given floating point value
- direction: It indicates which adjacent value is to be returned. If this number is smaller than
numthen smaller adjacent value is returned else greater adjacent value is returned.
nextAfter() Return Value
- Returns the adjacent float value.
- If any of the argument is NaN (Not a number) then NaN is returned.
- If both arguments are equal then second argument is returned.
- If num is (+ or -) Double.MIN_VALUE and direction is such that the smaller adjacent value is to be returned then zero with the sign of num is returned.
- If num is (+ or -) Double.MAX_VALUE and direction is such that the greater adjacent value is to be returned then infinity with the sign of num is returned.
- If num is infinity and direction is such that the smaller adjacent value is to be returned then Double.MAX_VALUE with the sign of num is returned.
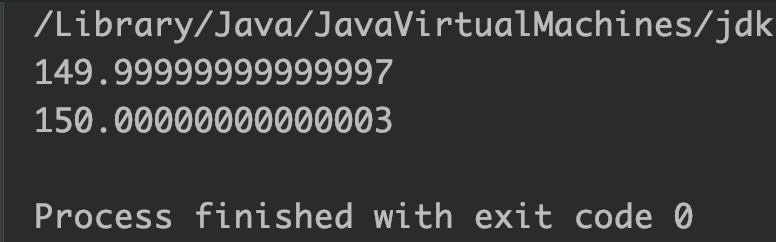
Example 1: Print adjacent floating point numbers
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double n1 = 150, n2 = 5 , n3 = 200;
// print the adjacent number of n1 towards n2
System.out.println(Math.nextAfter(n1, n2));
// print the adjacent number of n1 towards n3
System.out.println(Math.nextAfter(n1, n3));
}
}
Output:
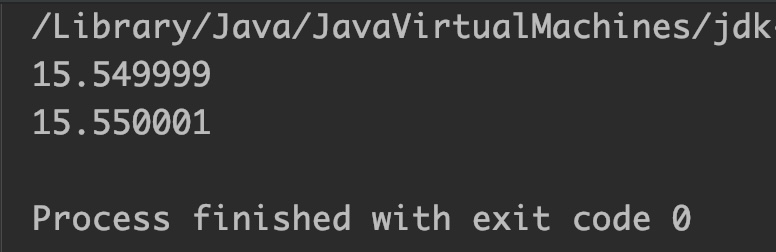
Example 2: Print adjacent of a float type number
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
float f = 15.55f;
double n1 =10, n2 = 20;
// print the adjacent of float number towards n1
System.out.println(Math.nextAfter(f, n1));
// print the adjacent of float number towards n2
System.out.println(Math.nextAfter(f, n2));
}
}
Output:
Example 3: Adjacent of Double Infinity
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double n = Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
double dir = 100;
System.out.println("Double Max value: "+Double.MAX_VALUE);
System.out.println(Math.nextAfter(n, dir));
}
}
Output:
