In Border layout we can add components (such as text fields, buttons, labels etc) to the five specific regions. These regions are called PAGE_START, LINE_START, CENTER, LINE_END, PAGE_END. Refer the diagram below to understand their location on a Frame.
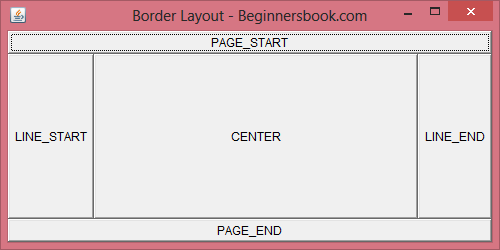
The diagram above is the output of below code, where I have added five buttons (which have same name as regions in which they have been placed) to the five regions of Border Layout. You can add any component of your choice in a similar manner.
package com.beginnersbook.layout;
import java.awt.*;
public class BorderDemo extends Frame{
// constructor
public BorderDemo(String title)
{
/* It would create the Frame by calling
* the constructor of Frame class.
*/
super(title);
//Setting up Border Layout
setLayout(new BorderLayout());
//Creating a button and adding it to PAGE_START area
Button b1 = new Button("PAGE_START");
add(b1, BorderLayout.PAGE_START);
/* Similarly creating 4 other buttons and adding
* them to other 4 areas of Border Layout
*/
Button b2= new Button("CENTER");
add(b2, BorderLayout.CENTER);
Button b3= new Button("LINE_START");
add(b3, BorderLayout.LINE_START);
Button b4= new Button("PAGE_END");
add(b4, BorderLayout.PAGE_END);
Button b5= new Button("LINE_END");
add(b5, BorderLayout.LINE_END);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{ BorderDemo screen =
new BorderDemo("Border Layout - Beginnersbook.com");
screen.setSize(500,250);
screen.setVisible(true);
}
}
Note: The name of buttons in the example above are intentionally set same as region names, this is just for educational purpose, you can name them as per your wish and requirement.
What if you want spaces among regions?
In the example above, we do not have any space among regions; however we can have horizontal as well as vertical space between regions. There are two ways to do it –
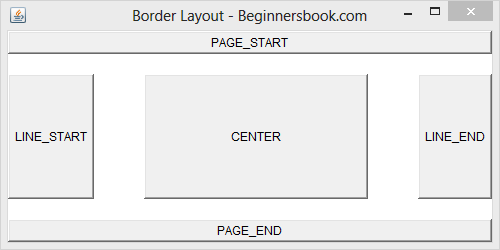
1) Notice the statement setLayout(new BorderLayout( )); in the example above, if you change it to this: setLayout(new BorderLayout(50,20)); then the output Frame would look like the image below. Here 50 is horizontal gap and 20 is vertical gap.
Method details:
public BorderLayout(int hgap, int vgap)
Constructs a border layout with the specified gaps between components. The horizontal gap is specified by hgap and the vertical gap is specified by vgap.
Parameters:
hgap – the horizontal gap.
vgap – the vertical gap.
2) You can also do it by using setHgap(int hgap) method for horizontal gap between components and setVgap(int vgap) method for vertical gap.
Aniket Jain says
I enjoy your website. It is really very much helpfull. Please add Card, Grid and Gridbag layout.