In this post, we will discuss the diamond operator enhancement introduced in Java SE 9.
What is a diamond operator?
Diamond operator was introduced as a new feature in java SE 7. The purpose of diamond operator is to avoid redundant code by leaving the generic type in the right side of the expression.
// This is before Java 7. We have to explicitly mention generic type // in the right side as well. List<String> myList = new ArrayList<String>(); // Since Java 7, no need to mention generic type in the right side // instead we can use diamond operator. Compiler can infer type. List<String> myList = new ArrayList<>();
Problem with the diamond operator while working with Anonymous Inner classes
Java 7 allowed us to use diamond operator in normal classes but it didn’t allow us to use them in anonymous inner classes. Lets take an example:
abstract class MyClass<T>{
abstract T add(T num, T num2);
}
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyClass<Integer> obj = new MyClass<>() {
Integer add(Integer x, Integer y) {
return x+y;
}
};
Integer sum = obj.add(100,101);
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
Output:
$javac JavaExample.java
JavaExample.java:7: error: cannot infer type arguments for MyClass
MyClass obj = new MyClass<>() {
^
reason: cannot use '<>' with anonymous inner classes
where T is a type-variable:
T extends Object declared in class MyClass
1 error
We got a compilation error when we ran the above code in Java SE 8.
Java 9 – Diamond operator enhancements
Java 9 improved the use of diamond operator and allows us to use the diamond operator with anonymous inner classes. Lets take the same example that we have seen above.
Running this code in Java SE 9
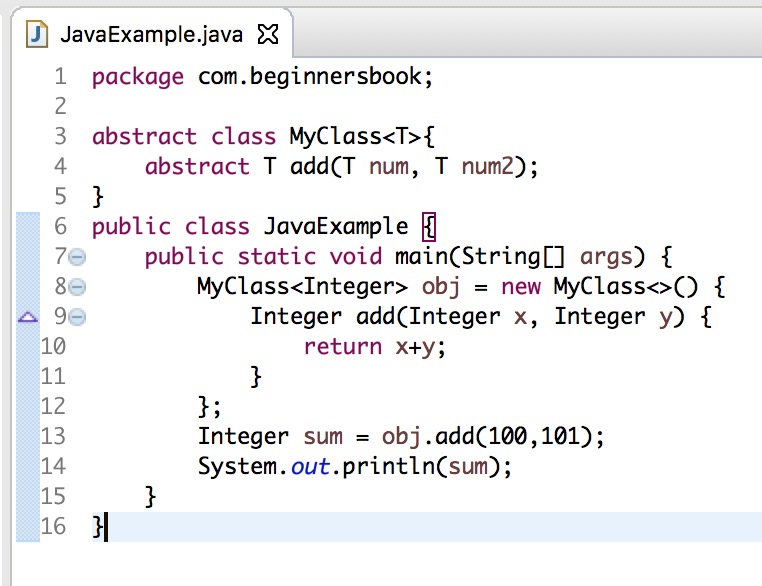
abstract class MyClass<T>{
abstract T add(T num, T num2);
}
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyClass<Integer> obj = new MyClass<>() {
Integer add(Integer x, Integer y) {
return x+y;
}
};
Integer sum = obj.add(100,101);
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
Output:
201
Screenshot of the above code in Eclipse Oxygen using jdk 9
Leave a Reply