The compareUnsigned() method compares two primitive int values without considering their sign. It is same as compare() method except that it doesn’t take sign into consideration while comparison.
Syntax of compareUnsigned() method
public static int compareUnsigned(int x, int y)
compareUnsigned() Parameters
x– First int number to comparey– Second int number to compare
compareUnsigned() Return Value
It returns:
- 0, if x == y
- a value less than 0, if x < y (unsigned)
- a value greater than 0, if x > y (unsigned)
Supported java versions: Java 1.8 and onwards
Example 1
public class JavaExample{
public static void main(String[] args){
int x = 32, y = -41; //negative 41
int x2 = 32, y2 = 41; // positive 41
//both the results are same because signs are not considered
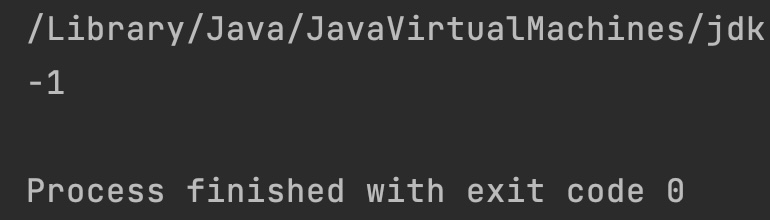
System.out.println(Integer.compareUnsigned(x, y));
System.out.println(Integer.compareUnsigned(x2, y2));
}
}
Output:
Example 2
import java.util.Scanner;
public class JavaExample{
public static void main(String[] args){
int x, y;
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter first int number: ");
x = scan.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter second int number: ");
y = scan.nextInt();
//compare user input values
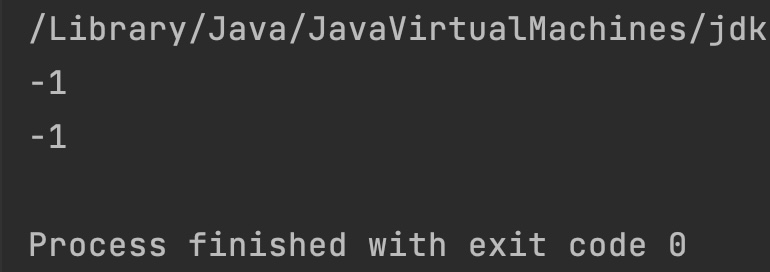
int result = Integer.compareUnsigned(x, y);
if(result ==0) {
System.out.println("Input numbers are equal");
}else if(result < 0){
System.out.println("First number is less than second");
}else{
System.out.println("First number is greater than second");
}
}
}
Output:

Example 3
public class JavaExample{
public static void main(String[] args){
Integer x = new Integer("100");
Integer y = new Integer("-200");
System.out.println(Integer.compareUnsigned(x, y));
}
}
Output: