Java Math.toRadians() method converts the given angle in degrees to radians. This the approximate conversion and in most of the cases, it is inexact.
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double degrees = 45;
// degrees to radians conversion
double radians = Math.toRadians(degrees);
System.out.println(radians);
}
}
Output:
0.7853981633974483
Syntax of Math.toRadians() method
Math.toRadians(90); // returns 1.5707963267948966
toRadians() Description
public static double toRadians(double degrees): It returns the approximate angle value in radians after the conversion.
toRadians() Parameters
- degrees: A double value that represents angle in degrees.
toRadians() Return Value
- The measurement of given argument
degreesin radians. - If the given argument is NaN (Not a number), then it returns NaN.
- If the given argument is zero, then it returns zero with the same sign.
- If the given argument is infinity, then it returns the infinity with the same sign.
Example 1: Degrees to Radians Conversion
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double d1 = 0;
double d2 = 180;
double d3 = -180;
System.out.println(Math.toRadians(d1));
System.out.println(Math.toRadians(d2));
System.out.println(Math.toRadians(d3));
}
}
Output:
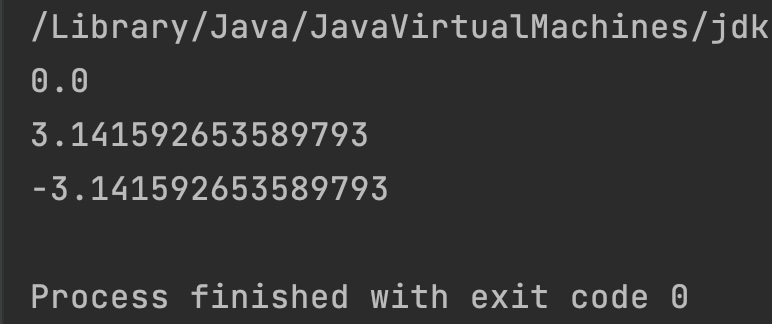
Example 2: Zero, NaN and Infinity to Radians
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double d1 = 0;
double d2 = 0.0/0; //NaN
double d3 = 5.0/0; //infinity
System.out.println(Math.toRadians(d1));
System.out.println(Math.toRadians(d2));
System.out.println(Math.toRadians(d3));
}
}
Output:

Example 3: Double max and min values to Radians
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
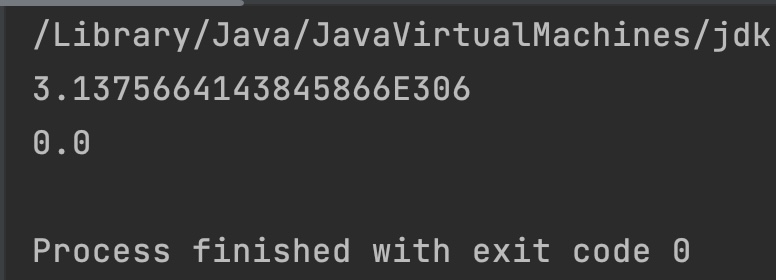
double d1 = Double.MAX_VALUE;
double d2 = Double.MIN_VALUE;
System.out.println(Math.toRadians(d1));
System.out.println(Math.toRadians(d2));
}
}
Output: