The append() method of Java StringBuffer class is used to append a specified value at the end of this character sequence.
Syntax of append() Method:
//append string "welcome" at the end of sb
sb.append("welcome");
//append the string "abc" at the end of sb
char[] chArray = {'a', 'b', 'c'}
sb.append(chArray);
Here, sb is an object of StringBuffer class.
append() Description
public StringBuffer append(char c): This method appends specified char c at the end of the char sequence represented by StringBuffer object. There are several variations of this method that allow various data types to be appended. These variations are:
public StringBuffer append(int i); public StringBuffer append(long l); public StringBuffer append(double d); public StringBuffer append(char c); public StringBuffer append(float f); public StringBuffer append(String str); public StringBuffer append(char[] str); public StringBuffer append(boolean b); public StringBuffer append(char[] str, int offset, int len); public StringBuffer append(CharSequence cs); public StringBuffer append(CharSequence cs, int start, int end); public StringBuffer append(Object obj); public StringBuffer append(StringBuffer sb);
append() Parameters
The append() method parameters are:
- offset: It specifies the position in the sequence.
- start: Integer index that represents the start of the subsequence that needs to be appended. (See example below)
- end: It represents the end of the subsequence that needs to be appended.
- i, l, d, f, ch, b: Represents the values of data types that needs to appended using append() method.
- str: String that is appended in the given StringBuffer character sequence.
append() Return Value
- Returns a StringBuffer instance that contains the appended value.
If specified offsets are invalid then this method throws IndexOutOfBoundsException.
Example 1: Append different data Types
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
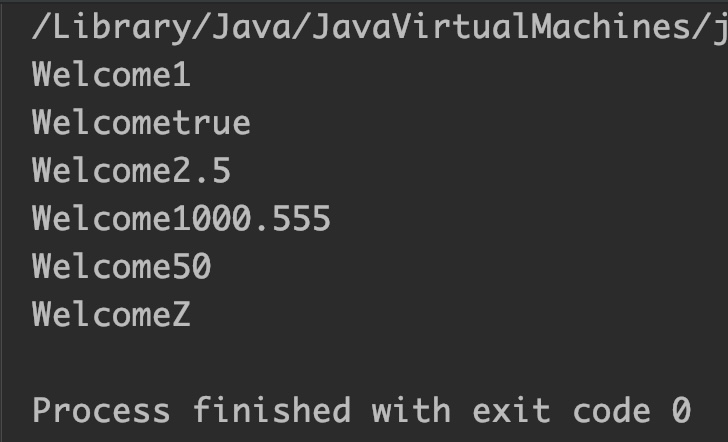
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer("Welcome");
sb.append(1);//append int
System.out.println(sb);
StringBuffer sb2 = new StringBuffer("Welcome");
sb2.append(true); //append boolean
System.out.println(sb2);
StringBuffer sb3 = new StringBuffer("Welcome");
sb3.append(2.5f); //append float
System.out.println(sb3);
StringBuffer sb4 = new StringBuffer("Welcome");
sb4.append(1000.555); //append double
System.out.println(sb4);
StringBuffer sb5 = new StringBuffer("Welcome");
sb5.append(50L); //append long
System.out.println(sb5);
StringBuffer sb6 = new StringBuffer("Welcome");
sb6.append('Z'); //append char
System.out.println(sb6);
}
}
Output:
Example 2: StringBuffer append(char[] str, int offset, int len)
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer("BeginnersBook");
System.out.println("Sequence :"+sb);
char[] chArray = {'a','b','c','.','c','o','m'};
// appending elements of char array from 4th till 7th
sb.append(chArray, 3, 4);
System.out.println("New Sequence: " + sb);
}
}
Output:

Example 3: StringBuffer append(CharSequence cs, int start, int end)
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
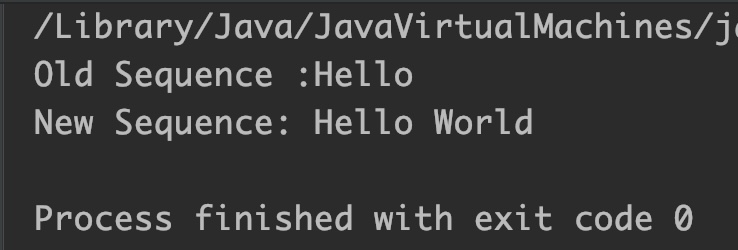
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer("Hello");
System.out.println("Old Sequence :"+sb);
CharSequence cs = "My World";
// appending chars of given char sequence from 2 to 8th
//endIndex is exclusive. This means char at 8th index is
//not included in the append operation.
sb.append(cs, 2, 8);
System.out.println("New Sequence: " + sb);
}
}
Output:
Example 4: StringBuffer append(Object obj)
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
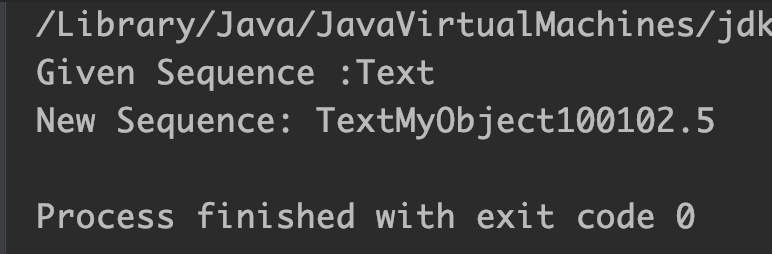
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer("Text");
System.out.println("Given Sequence :"+sb);
Object obj = "MyObject";//string object
Object obj2 = 100L; //long object
Object obj3 = 102.5f; //float object
//appending All three objects at the end of sequence
sb.append(obj);
sb.append(obj2);
sb.append(obj3);
System.out.println("New Sequence: " + sb);
}
}
Output:
Example 5: Append StringBuilder into StringBuffer
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
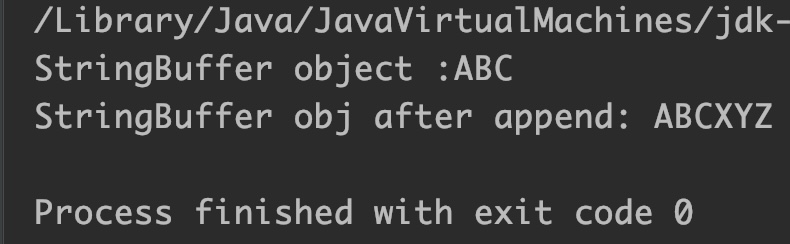
StringBuffer sBuffer = new StringBuffer("ABC");
System.out.println("StringBuffer object :"+sBuffer);
StringBuilder sBuilder =new StringBuilder("XYZ");
// appending string builder
sBuffer.append(sBuilder);
// print StringBuffer obj
System.out.println("StringBuffer obj after append: " + sBuffer);
}
}
Output: