Java StringBuffer charAt() method returns the character present at the given index. In this tutorial, we will discuss the charAt() method with examples.
Syntax of charAt() method
sb.charAt(0); //returns the first char sb.charAt(sb.length()-1); //returns the last char
Here, sb is an object of StringBuffer class.
charAt() Description
public char charAt(int index): This method returns the character present at the specified index. The first char of StringBuffer is at index 0, second one is at index 1 and so on.
charAt() Parameters
The charAt() method of Java StringBuffer class takes a single parameter:
- index: The character present at this index is returned by the
charAt()method
The index argument must be greater than or equal to 0, and less than the length of the sequence, otherwise it would throw IndexOutOfBoundsException
charAt() Return Value
- Returns the character present at the index that we pass as an argument to the
charAt()method.
Example 1: Print all characters of a string
class JavaExample{
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer("Hello");
System.out.println("String is: "+sb);
for(int i=0; i<sb.length(); i++){
System.out.println("Character at index "+i+
" is: "+sb.charAt(i));
}
}
}
Output:

Example 2: Print first and last character of a string
class JavaExample{
public static void main(String[] args) {
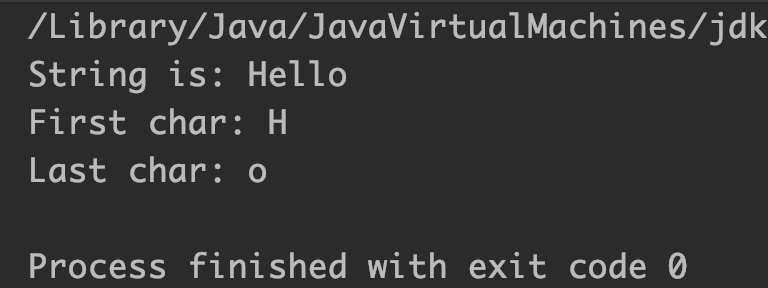
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer("Hello");
System.out.println("String is: "+sb);
//first character of the sequence
System.out.println("First char: "+sb.charAt(0));
//first character of the sequence
System.out.println("Last char: "+sb.charAt(sb.length()-1));
}
}
Output:
Example 3: Print characters at given index
class JavaExample{
public static void main(String[] args) {
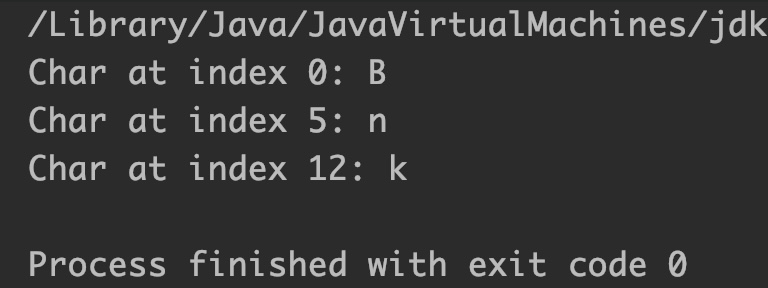
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer("BeginnersBook");
System.out.println("Char at index 0: "+sb.charAt(0));
System.out.println("Char at index 5: "+sb.charAt(5));
System.out.println("Char at index 12: "+sb.charAt(12));
}
}
Output:
Example 4: Given index is negative
class JavaExample{
public static void main(String[] args) {
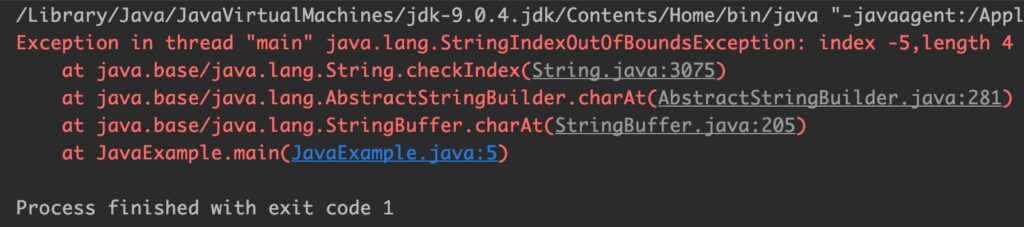
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer("Text");
//negative index in charAt()
System.out.println(sb.charAt(-5));
}
}
Output:
Example 5: Index is greater than or equal to the length of string
class JavaExample{
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer("hello");
//The string 'hello' has index from 0 to 4
//so no char present at the index 5
System.out.println(sb.charAt(5));
}
}
Output:
