Array is a collection of elements of same type. For example an int array contains integer elements and a String array contains String elements. The elements of Array are stored in contiguous locations in the memory. Arrays in Java are based on zero-based index system, which means the first element is at index 0.
This is how an array looks like:
int number[] = new int[10]
Here number is the array name. The type of the array is integer, which means it can store integer values. The size of the array is 10.
Array works on an index-based system. In the above array, number[0] represents the first element of the array, number[1] represents the second element of the array and so on. The index of array starts from 0 and ends at array_size-1. In the above example, the index of first element is 0 and index of 10th element is 9.
Advantages of Array
Better performance: Since array works on a index based system, it is easier to search an element in the array, thus it gives better performance for various operations.
Multidimensional: Unlike ArrayList which is single dimensional, array are multidimensional such as 2D array, 3D array etc.
Faster access: Accessing an element is easy in array.
Disadvantages of Array:
Fixed Size: The size of the array is fixed, which cannot be increased later.
Allows only similar type elements: Arrays are homogeneous, they don’t allow different type values, for example an int array cannot hold string elements, similarly a String array cannot hold integer elements.
Insertion and delegation requires shifting of elements.
Declaration, Instantiation and Initialization of Array in Java
This is how we declare, instantiate and initialize an array. I have covered this in separate tutorial as well: Declaration and initialization of an Array.
int number[]; //array declaration number[] = new int[10]; //array instantiation number[0] = 10; //array Initialization number[1] = 20; //array Initialization
We can also declare an array like this: All the three following syntax are valid for array declaration.
int[] number; int []number; int number[];
Example:
The following example demonstrates, how we declared an int array, initialized it with integers and print the elements of the array using for loop.
Note: You can see that we have used length property of array to find the size of the array. The length property of array returns the number of elements present in the array.
public class JavaExample{
public static void main(String args[]){
//array declaration, instantiation and initialization
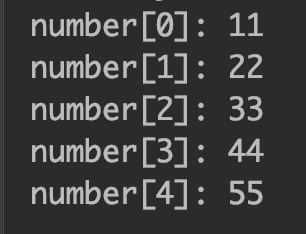
int number[] = {11, 22, 33, 44, 55};
//print array elements
//length property return the size of the array
for(int i=0;i<number.length;i++)
System.out.println("number["+i+"]: "+number[i]);
}
}
Output:
Types of array in Java
1. Single Dimensional Array
2. Multidimensional Array
1. Single dimensional array
public class JavaExample{
public static void main(String args[]){
//array declaration
String names[] = new String[5];
//array initialization
names[0]="Chaitanya";
names[1]="Ajeet";
names[2]="Rahul";
names[3]="Shivam";
names[4]="Rohit";
//print array elements
for(int i=0;i<names.length;i++)
System.out.println("names["+i+"]: "+names[i]);
}
}
Output:
names[0]: Chaitanya names[1]: Ajeet names[2]: Rahul names[3]: Shivam names[4]: Rohit
2. Multidimensional array
Multidimensional array declaration:
This is how you can declare a multidimensional array: All the four syntax are valid multidimensional array declaration.
int[][] arr; int [][]arr; int arr[][]; int []arr[];
Instantiate Multidimensional Array in Java
Number of elements in multidimensional array = number of rows*number of columns.
The following array can store upto 2*3 = 6 elements.
int[][] arr=new int[2][3]; //2 rows and 3 columns
Initialize Multidimensional Array in Java
arr[0][0]=11; arr[0][1]=22; arr[0][2]=33; arr[1][0]=44; arr[1][1]=55; arr[1][2]=66;
Example:
public class JavaExample{
public static void main(String args[]){
//two rows and three columns
int arr[][]={{11,22,33},{44,55,66}};
//outer loop 0 till number of rows
for(int i=0;i<2;i++){
//inner loop from 0 till number of columns
for(int j=0;j<3;j++){
System.out.print(arr[i][j]+" ");
}
//new line after each row
System.out.println();
}
}
}
Output:

Print an Array elements using for-each loop
In the previous examples, we have seen how to print array elements using for loop. There is another way to print Array elements without using array length property.
public class JavaExample{
public static void main(String args[]){
//String array
String names[]={"Chaitanya", "Ajeet", "Rahul", "Hari"};
//print array elements using for-each loop
for(String str:names)
System.out.println(str);
//int array
int numbers[]={1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
//print array elements using for-each loop
for(int num:numbers)
System.out.println(num);
}
}
Output:
Chaitanya Ajeet Rahul Hari 1 2 3 4 5
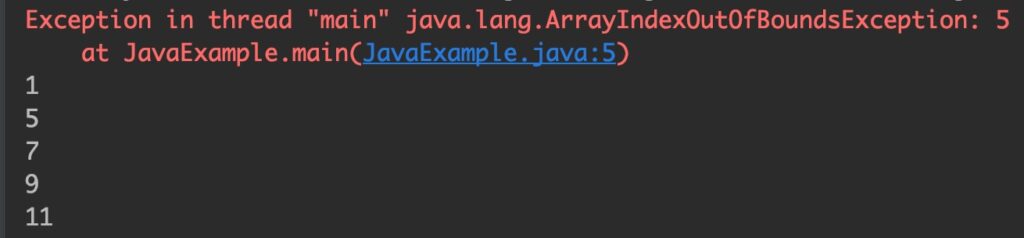
Exception: ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException occurs when we access an array with an invalid index. This happens when the index is either negative or greater than or equal to the size of the array.
public class JavaExample{
public static void main(String args[]){
int number[]={1, 5, 7, 9, 11};
for(int i=0;i<=number.length;i++){
System.out.println(number[i]);
}
}
}
Output:
Recommended Articles:
1) Java program to print number of elements in an array
2) Java program to remove duplicate elements in an array
3) Java program to left rotate the elements of an array
4) Java program to right rotate the elements of an array
5) Java program to find smallest number in an array
6) Java program to find largest element of an array
7) Java program to count the frequency of each element in an array
8) Java program to print the duplicate elements of an array
9) Java program to copy all elements from one array to another array
10) Java program to print the elements of an array present on odd position
11) Java program to print the elements of an array present on even position
12) Java program to add two matrix using multidimensional arrays
13) Java program to check whether two matrices are equal
14) Java program to reverse an array
15) Random shuffling of an array in Java
16) Java program to sort an array
17) Java program to calculate average using array
18) Sorting char array in Java
Leave a Reply