Ternary operator is the only operator in java that takes three operands. A ternary operator starts with a condition followed by a question mark (?), then an expression to execute if the condition is ‘true; followed by a colon (:), and finally the expression to execute if the condition is ‘false’. This operator is frequently used as a one line replacement for if…else statement.
Syntax of Ternary Operator
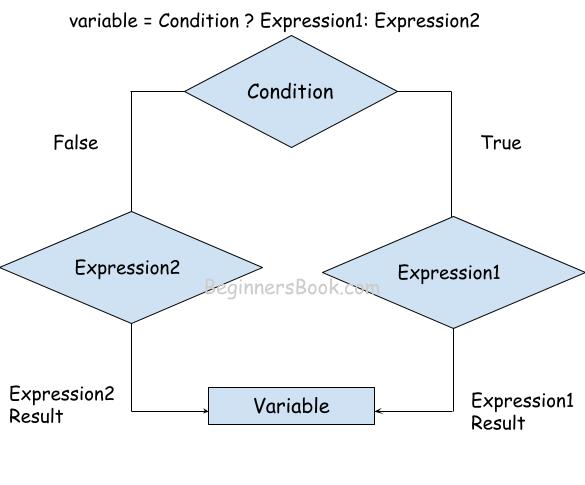
variable = Condition ? Expression1: Expression2
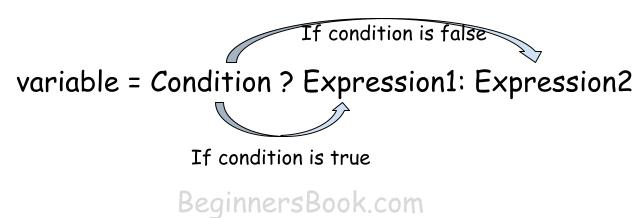
If condition is true, the Expression1 executes.
If condition is false, the Expression2 executes.
For example:
class JavaExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int age = 16;
boolean isAdult = age >= 18 ? true : false;
System.out.println("Can Vote? "+isAdult);
}
}
Output:
Can Vote? false
Equivalent if..else statement:
class JavaExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int age = 16;
if(age>=18){
System.out.println("Can Vote? true");
}
else{
System.out.println("Can Vote? false");
}
}
}
You can see that a one-liner ternary operation replaced the complete if..else logic we had to write in the second example.
The ternary operator is widely used in programming as it is more readable and simple. The only thing to remember is the syntax of ternary operator, which you can easily remember by practicing few java programs such as:
- Java Program to find the smallest of three numbers using Ternary Operator
- Java program to find largest of three numbers using Ternary operator
Ternary operator Flowchart
Ternary operator Example
Displaying whether the given number is positive or negative using Ternary Operator.
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// declared and initialized a int variable
int num = -101;
//Using ternary operator, we are assigning the "Positive"
//or "Negative" String value to the String variable 'sign'
//If num>0 then "Positive" is assigned to 'sign' else "Negative"
String sign = (num > 0) ? "Positive" : "Negative";
//Display output
System.out.println(num+ " is a "+sign+ " Number");
}
}
Output:
-101 is a Negative Number
Example 2: Here, we are checking whether the given number is even or odd using ternary operator.
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num = 9;
//Checking "even" or "odd" using ternary operator
//If num % 2 == 0 then "Even" else "Odd"
String strEvenOdd = (num % 2==0) ? "Even Number" : "Odd Number";
//Display output
System.out.println(strEvenOdd);
}
}
Output:
Odd Number
Nested Ternary Operators
We can use a ternary operator inside another ternary operator. This is called nesting of ternary operators. In the example, we are checking whether a given year is leap year or not using nested ternary operator.
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// This variable stores the year that we need to check
int year = 2004;
boolean isLeap;
isLeap = ((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) ?
true : (year % 400 == 0) ? true : false);
// Print the result
System.out.println(year + " is a leap year: " + isLeap);
}
}
Output:
2004 is a leap year: true
In the above example, we used the ternary operator like this:
((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) ?
true : (year % 400 == 0) ? true : false)
Here,(year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) : This is the first test condition that checks if the year is perfectly divisible by 4 and 100. If this condition is true, then true value is assigned to isLeap variable.
(year % 400 == 0) ? true : false) : If first condition returns false, then this expression is executed. Here instead of expression, we have used another ternary operator. This only executes if main condition returns false. Here we are checking if the year is divisible by 400 or not, if it is then the year is leap year else not a leap year.