Java Math.nextDown() method returns floating point number adjacent to the passed argument, in the direction of negative infinity.
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double d = 12345;
float f = 8.88f;
System.out.println(Math.nextDown(d));
System.out.println(Math.nextDown(f));
}
}
Output:
12344.999999999998 8.879999
Syntax of Math.nextDown() method
Math.nextDown(12.25f); //returns 12.249999
nextDown() Description
public static double nextDown(double d): Returns floating point value adjacent to d, towards negative infinity. This is equivalent to nextAfter(d, Double.NEGATIVE_INFINITY). However it faster compared to nextAfter() method.
public static float nextDown(float f): Returns floating point value adjacent to passed float argument f, towards negative infinity. This is equivalent to nextAfter(d, Float.NEGATIVE_INFINITY). However it faster compared to nextAfter() method.
nextDown() Parameters
- d: Double value whose adjacent value to be determined.
- f: Float value whose adjacent value to be determined.
nextDown() Return Value
- Adjacent floating value towards negative infinity.
- If the argument is NaN (Not a number) then it returns NaN.
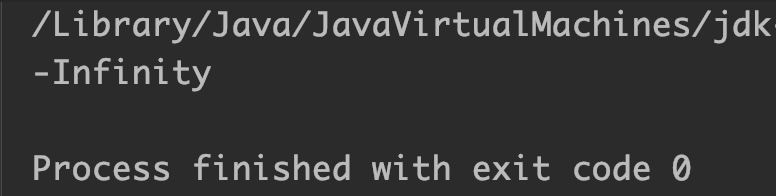
- If the argument is negative infinity, then it returns negative infinity.
- If the passed argument is zero, it returns -Double.MIN_VALUE for double type argument or -Float.MIN_VALUE for float type argument.
Example 1
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double d = 500;
float f = 6.51f;
System.out.println(Math.nextDown(d)); //towards negative infinity
System.out.println(Math.nextDown(f)); //towards negative infinity
}
}
Output:
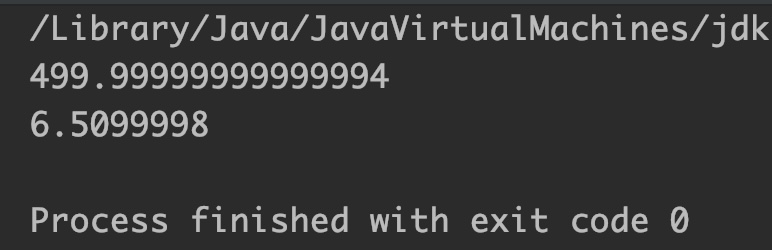
Example 2
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double d = 0.0/0; //NaN
System.out.println(Math.nextDown(d));
}
}
Output:
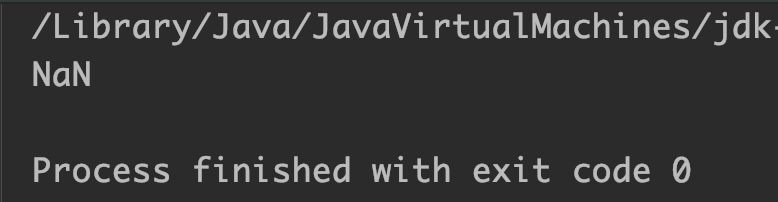
Example 3
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double d = 0; // zero double value
float f = 0.0f; //zero float value
//This will return -Double.MIN_VALUE
System.out.println(Math.nextDown(d));
//This will return -Float.MIN_VALUE
System.out.println(Math.nextDown(f));
}
}
Output:
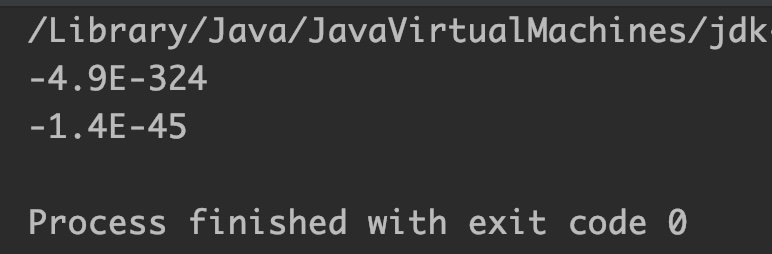
Example 4
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double d = Double.NEGATIVE_INFINITY;
System.out.println(Math.nextDown(d));
}
}
Output: