Java Math.copySign() method returns the first argument with the sign of second argument. In simple words, it copies the sign of second argument and replaces the sign of first argument with this copied sign.
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double n1 = 150.55, n2 = -32.56;
System.out.println(Math.copySign(n1, n2));
}
}
Output:
-150.55
Syntax of Math.copySign() method
Math.copySign(15, -7); //returns -15.0
copySign() Description
public static double copySign(double n1, double n2): Returns the double value n1 with the sign of n2 value.
public static float copySign(float n1, float n2): Returns the float value n1 with the sign of n2.
copySign() Parameters
It takes two parameters:
- n1: First argument, whose magnitude is to be returned as result.
- n2: Second argument, whose sign is to be returned with the magnitude of first argument.
copySign() Return Value
- Value with the magnitude of first argument with the sign of second argument.
Example 1: Copy sign from one double to another double number
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double n1 = 150.55, n2 = -32.56;
//copy sign of n2 to n1
System.out.println(Math.copySign(n1, n2));
}
}
Output:
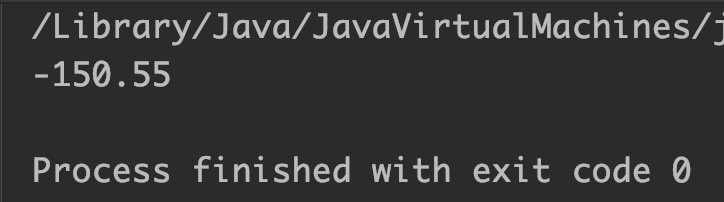
Example 2: Copy sign from one float to another float number
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
float f1 = -3, f2 =8;
System.out.println(Math.copySign(f1, f2));
}
}
Output:
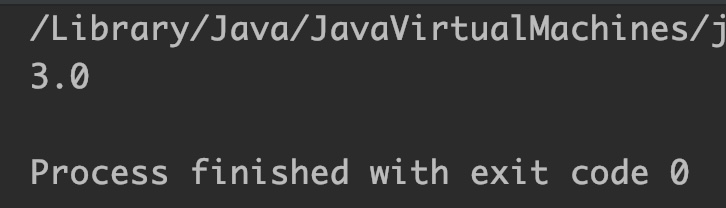
Example 3: Copy sign from zero
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
float f1 = -5.5f, f2 =0.0f;
System.out.println(Math.copySign(f1, f2));
}
}
Output:
