Java StringBuffer trimToSize() method is used to reduce the capacity of StringBuffer instance, if possible. This method checks for non-utilized allocated space, it frees up the storage to optimize the buffer size.
Syntax of trimToSize() method
sb.trimToSize() //free up non-utilized buffer
Here, sb is an object of StringBuffer class.
trimToSize() Description
public void trimToSize(): It optimizes the buffer memory by reducing the space that is currently allocated to the current StringBuffer instance.
trimToSize() Parameters
- It does not take any parameter.
trimToSize() Return Value
- The return type of this method is void as it does not return anything.
Example 1
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
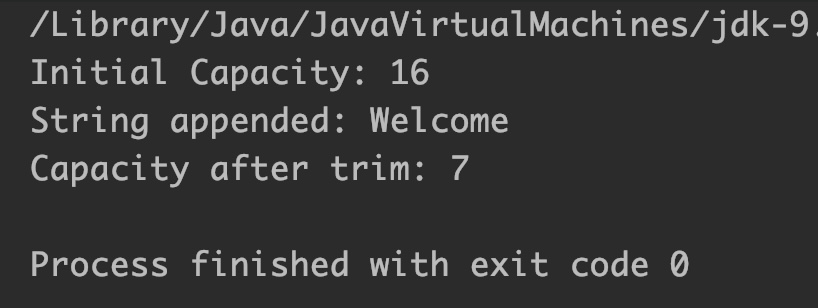
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
System.out.println("Initial Capacity: "+sb.capacity());
//append string
sb.append("Welcome");
System.out.println("String appended: "+sb);
//cleanup buffer, non-utilized 9 spaces are trimmed
sb.trimToSize();
System.out.println("Capacity after trim: "+sb.capacity());
}
}
Output:
Example 2
public class JavaExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
System.out.println("Initial Capacity: "+sb.capacity());
//If current capacity is less than 20 then it will increase
//old capacity = (new capacity * 2) +2
sb.ensureCapacity(20); //new = 16*2 +2 =34
System.out.println("Capacity after ensureCapacity: "+sb.capacity());
//append string
sb.append("Text");
System.out.println("String appended: "+sb);
//cleanup buffer
sb.trimToSize();
System.out.println("Capacity after trim: "+sb.capacity());
}
}
Output:
