Java Math.subtractExact() method returns the difference of its arguments. It subtracts the value of second argument from the first argument and returns the result.
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int i = 20, i2 = 10;
long l = 10000L, l2 = 15000L;
System.out.println(Math.subtractExact(i, i2));
System.out.println(Math.subtractExact(l, l2));
}
}
Output:
10 -5000
Syntax of Math.subtractExact() method
Math.subtractExact(100, 50); //returns 50
subtractExact() Description
public static int subtractExact(int x, int y): Returns the difference of its two integer arguments. It throws ArithmeticException, if one of the argument is Integer.MIN_VALUE.
public static long subtractExact(long x, long y): Returns the difference of its two long arguments. It throws ArithmeticException, if one of the argument is Long.MIN_VALUE.
subtractExact() Parameters
It takes two parameters:
- x: First argument
- y: Second argument
subtractExact() Return Value
- It subtracts second argument
yfrom the first argumentxand returns(x-y)as result.
Example 1: Difference of two int arguments
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int x = 10, y = 20; //two int variables
System.out.println("Difference: "+Math.subtractExact(x, y));
}
}
Output:
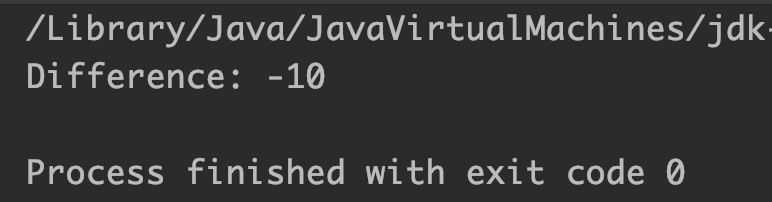
Example 2: Difference of two long arguments
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
long x = 7000L, y = 5000L; //two long variables
System.out.println("Difference: "+Math.subtractExact(x, y));
}
}
Output:
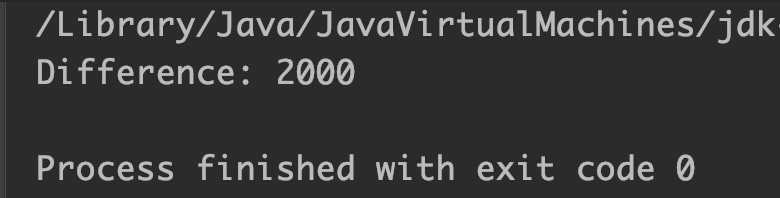
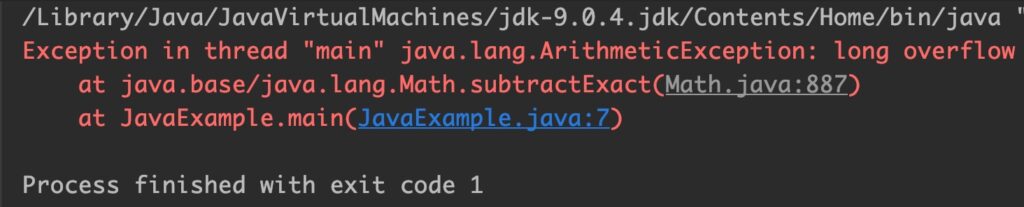
Example 3: Integer Overflow
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int x = 100;
int y = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
System.out.println(Math.subtractExact(x, y));
}
}
Output:
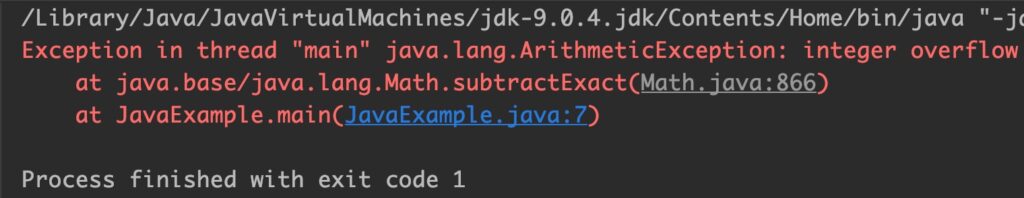
Example 4: Long Overflow
public class JavaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
long x = 10000L;
long y = Long.MIN_VALUE;
System.out.println(Math.subtractExact(x, y));
}
}
Output: